Genetic prion diseases presenting as frontotemporal lobar degeneration: clinical features and diagnostic challenge Article Swipe
 YOU?
·
· 2023
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.061751
YOU?
·
· 2023
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.061751
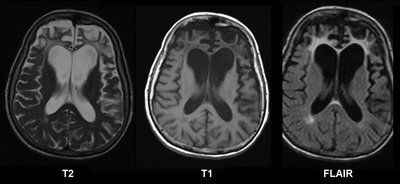
Background Elucidate the clinical and ancillary feature of genetic prion diseases (gPrDs) presenting with frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) in order to aid early identification, diagnosis, and referral for genotype testing. Method Global data of gPrDs presenting with FTLD caused by prion protein gene (PRNP) mutations were collected from literature review and our records. Fifty‐one cases of typical FTLD and 136 of prion diseases admitted to our institution were included as controls. Clinical and ancillary data of the different groups were compared. Result Forty‐nine cases of gPrDs presenting with FTLD were identified, 23 of which were female. Twenty‐three mutations in PRNP have been reported to be associated with the FTLD, with P39L being the most commonly reported, seen in 4 families with 5 cases. Compared to FTLD or prion diseases, gPrDs presenting with FTLD is characterized by earlier onset age (median: 45 vs. 61/60 years) and stronger family history (81.6% vs. 27.5/13.2%). In addition, gPrDs presenting with FTLD exhibited shorter duration (median: 5 vs. 8 years), and a higher rate of clinical and ancillary features of prion diseases compared to FTLD. Compared to prion diseases, gPrDs presenting with FTLD had a longer duration of symptoms (median: 5 vs. 1.1 years), higher rates of frontotemporal atrophy (89.7% vs. 3.3%), lower rates of periodic short‐wave complexes on EEG (0% vs. 29.4%), and hyperintensity on MRI (25.0% vs. 83.0%). The frequency of the Val allele for codon 129 in PRNP carriers with FTLD was significantly higher than that reported in literature for gPrDs (33.3% vs. 19.2%). Conclusion GPrDs presenting with FTLD is characterized by early‐onset, strong family history, high frequency of the Val allele for codon 129 in PRNP. The clinical features of GPrDs presenting with FTLD is intermediate of the two distinct conditions, while the auxiliary features were closer to that of FTLD. Patients with these characteristics need to be considered for PRNP genotype testing.
Related Topics
- Type
- article
- Language
- en
- Landing Page
- https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.061751
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/alz.061751
- OA Status
- bronze
- Related Works
- 10
- OpenAlex ID
- https://openalex.org/W4380883316
Raw OpenAlex JSON
- OpenAlex ID
-
https://openalex.org/W4380883316Canonical identifier for this work in OpenAlex
- DOI
-
https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.061751Digital Object Identifier
- Title
-
Genetic prion diseases presenting as frontotemporal lobar degeneration: clinical features and diagnostic challengeWork title
- Type
-
articleOpenAlex work type
- Language
-
enPrimary language
- Publication year
-
2023Year of publication
- Publication date
-
2023-06-01Full publication date if available
- Authors
-
Zhongyun Chen, Liyong Wu, Min Kyung Chu, Yu Kong, Kexin Xie, Yue CuiList of authors in order
- Landing page
-
https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.061751Publisher landing page
- PDF URL
-
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/alz.061751Direct link to full text PDF
- Open access
-
YesWhether a free full text is available
- OA status
-
bronzeOpen access status per OpenAlex
- OA URL
-
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/alz.061751Direct OA link when available
- Concepts
-
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration, PRNP, Medicine, Atrophy, Frontotemporal dementia, Pediatrics, Pathology, Internal medicine, Dementia, Disease, Prion proteinTop concepts (fields/topics) attached by OpenAlex
- Cited by
-
0Total citation count in OpenAlex
- Related works (count)
-
10Other works algorithmically related by OpenAlex
Full payload
| id | https://openalex.org/W4380883316 |
|---|---|
| doi | https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.061751 |
| ids.doi | https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.061751 |
| ids.openalex | https://openalex.org/W4380883316 |
| fwci | 0.0 |
| type | article |
| title | Genetic prion diseases presenting as frontotemporal lobar degeneration: clinical features and diagnostic challenge |
| biblio.issue | S4 |
| biblio.volume | 19 |
| biblio.last_page | |
| biblio.first_page | |
| topics[0].id | https://openalex.org/T11335 |
| topics[0].field.id | https://openalex.org/fields/13 |
| topics[0].field.display_name | Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology |
| topics[0].score | 0.9998000264167786 |
| topics[0].domain.id | https://openalex.org/domains/1 |
| topics[0].domain.display_name | Life Sciences |
| topics[0].subfield.id | https://openalex.org/subfields/1312 |
| topics[0].subfield.display_name | Molecular Biology |
| topics[0].display_name | Prion Diseases and Protein Misfolding |
| topics[1].id | https://openalex.org/T13481 |
| topics[1].field.id | https://openalex.org/fields/28 |
| topics[1].field.display_name | Neuroscience |
| topics[1].score | 0.9851999878883362 |
| topics[1].domain.id | https://openalex.org/domains/1 |
| topics[1].domain.display_name | Life Sciences |
| topics[1].subfield.id | https://openalex.org/subfields/2808 |
| topics[1].subfield.display_name | Neurology |
| topics[1].display_name | Neurological diseases and metabolism |
| topics[2].id | https://openalex.org/T10499 |
| topics[2].field.id | https://openalex.org/fields/27 |
| topics[2].field.display_name | Medicine |
| topics[2].score | 0.9797000288963318 |
| topics[2].domain.id | https://openalex.org/domains/4 |
| topics[2].domain.display_name | Health Sciences |
| topics[2].subfield.id | https://openalex.org/subfields/2745 |
| topics[2].subfield.display_name | Rheumatology |
| topics[2].display_name | Folate and B Vitamins Research |
| is_xpac | False |
| apc_list.value | 4000 |
| apc_list.currency | USD |
| apc_list.value_usd | 4000 |
| apc_paid | |
| concepts[0].id | https://openalex.org/C2776939681 |
| concepts[0].level | 5 |
| concepts[0].score | 0.9245712757110596 |
| concepts[0].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q18579 |
| concepts[0].display_name | Frontotemporal lobar degeneration |
| concepts[1].id | https://openalex.org/C2778147599 |
| concepts[1].level | 4 |
| concepts[1].score | 0.7558779716491699 |
| concepts[1].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q14881255 |
| concepts[1].display_name | PRNP |
| concepts[2].id | https://openalex.org/C71924100 |
| concepts[2].level | 0 |
| concepts[2].score | 0.5549286603927612 |
| concepts[2].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q11190 |
| concepts[2].display_name | Medicine |
| concepts[3].id | https://openalex.org/C2781172350 |
| concepts[3].level | 2 |
| concepts[3].score | 0.5475902557373047 |
| concepts[3].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q194520 |
| concepts[3].display_name | Atrophy |
| concepts[4].id | https://openalex.org/C2778641062 |
| concepts[4].level | 4 |
| concepts[4].score | 0.48815494775772095 |
| concepts[4].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q18592 |
| concepts[4].display_name | Frontotemporal dementia |
| concepts[5].id | https://openalex.org/C187212893 |
| concepts[5].level | 1 |
| concepts[5].score | 0.4310040771961212 |
| concepts[5].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q123028 |
| concepts[5].display_name | Pediatrics |
| concepts[6].id | https://openalex.org/C142724271 |
| concepts[6].level | 1 |
| concepts[6].score | 0.4217299818992615 |
| concepts[6].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q7208 |
| concepts[6].display_name | Pathology |
| concepts[7].id | https://openalex.org/C126322002 |
| concepts[7].level | 1 |
| concepts[7].score | 0.3428822159767151 |
| concepts[7].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q11180 |
| concepts[7].display_name | Internal medicine |
| concepts[8].id | https://openalex.org/C2779483572 |
| concepts[8].level | 3 |
| concepts[8].score | 0.3152756690979004 |
| concepts[8].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q83030 |
| concepts[8].display_name | Dementia |
| concepts[9].id | https://openalex.org/C2779134260 |
| concepts[9].level | 2 |
| concepts[9].score | 0.3106120824813843 |
| concepts[9].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q12136 |
| concepts[9].display_name | Disease |
| concepts[10].id | https://openalex.org/C3019804061 |
| concepts[10].level | 3 |
| concepts[10].score | 0.26282167434692383 |
| concepts[10].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q14881255 |
| concepts[10].display_name | Prion protein |
| keywords[0].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/frontotemporal-lobar-degeneration |
| keywords[0].score | 0.9245712757110596 |
| keywords[0].display_name | Frontotemporal lobar degeneration |
| keywords[1].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/prnp |
| keywords[1].score | 0.7558779716491699 |
| keywords[1].display_name | PRNP |
| keywords[2].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/medicine |
| keywords[2].score | 0.5549286603927612 |
| keywords[2].display_name | Medicine |
| keywords[3].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/atrophy |
| keywords[3].score | 0.5475902557373047 |
| keywords[3].display_name | Atrophy |
| keywords[4].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/frontotemporal-dementia |
| keywords[4].score | 0.48815494775772095 |
| keywords[4].display_name | Frontotemporal dementia |
| keywords[5].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/pediatrics |
| keywords[5].score | 0.4310040771961212 |
| keywords[5].display_name | Pediatrics |
| keywords[6].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/pathology |
| keywords[6].score | 0.4217299818992615 |
| keywords[6].display_name | Pathology |
| keywords[7].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/internal-medicine |
| keywords[7].score | 0.3428822159767151 |
| keywords[7].display_name | Internal medicine |
| keywords[8].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/dementia |
| keywords[8].score | 0.3152756690979004 |
| keywords[8].display_name | Dementia |
| keywords[9].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/disease |
| keywords[9].score | 0.3106120824813843 |
| keywords[9].display_name | Disease |
| keywords[10].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/prion-protein |
| keywords[10].score | 0.26282167434692383 |
| keywords[10].display_name | Prion protein |
| language | en |
| locations[0].id | doi:10.1002/alz.061751 |
| locations[0].is_oa | True |
| locations[0].source.id | https://openalex.org/S108427512 |
| locations[0].source.issn | 1552-5260, 1552-5279 |
| locations[0].source.type | journal |
| locations[0].source.is_oa | False |
| locations[0].source.issn_l | 1552-5260 |
| locations[0].source.is_core | True |
| locations[0].source.is_in_doaj | False |
| locations[0].source.display_name | Alzheimer s & Dementia |
| locations[0].source.host_organization | https://openalex.org/P4310320595 |
| locations[0].source.host_organization_name | Wiley |
| locations[0].source.host_organization_lineage | https://openalex.org/P4310320595 |
| locations[0].source.host_organization_lineage_names | Wiley |
| locations[0].license | |
| locations[0].pdf_url | https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/alz.061751 |
| locations[0].version | publishedVersion |
| locations[0].raw_type | journal-article |
| locations[0].license_id | |
| locations[0].is_accepted | True |
| locations[0].is_published | True |
| locations[0].raw_source_name | Alzheimer's & Dementia |
| locations[0].landing_page_url | https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.061751 |
| indexed_in | crossref |
| authorships[0].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5056917368 |
| authorships[0].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6708-8391 |
| authorships[0].author.display_name | Zhongyun Chen |
| authorships[0].countries | CN |
| authorships[0].affiliations[0].institution_ids | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[0].affiliations[0].raw_affiliation_string | Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China |
| authorships[0].institutions[0].id | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[0].institutions[0].ror | https://ror.org/013xs5b60 |
| authorships[0].institutions[0].type | education |
| authorships[0].institutions[0].lineage | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[0].institutions[0].country_code | CN |
| authorships[0].institutions[0].display_name | Capital Medical University |
| authorships[0].author_position | first |
| authorships[0].raw_author_name | Zhongyun Chen |
| authorships[0].is_corresponding | True |
| authorships[0].raw_affiliation_strings | Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China |
| authorships[1].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5059650235 |
| authorships[1].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0684-6248 |
| authorships[1].author.display_name | Liyong Wu |
| authorships[1].countries | CN |
| authorships[1].affiliations[0].institution_ids | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[1].affiliations[0].raw_affiliation_string | Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China |
| authorships[1].affiliations[1].institution_ids | https://openalex.org/I4210087417 |
| authorships[1].affiliations[1].raw_affiliation_string | Beijing Key Laboratory of Geriatric Cognitive Disorders and Neurodegenerative, Beijing China |
| authorships[1].affiliations[2].institution_ids | https://openalex.org/I4210087417 |
| authorships[1].affiliations[2].raw_affiliation_string | Beijing Key Laboratory of Geriatric Cognitive Disorders and Neurodegenerative, Beijing, China |
| authorships[1].affiliations[3].institution_ids | https://openalex.org/I4210115644 |
| authorships[1].affiliations[3].raw_affiliation_string | Center of Alzheimer’s Disease, Beijing Institute for Brain Disorders, Beijing China |
| authorships[1].institutions[0].id | https://openalex.org/I4210087417 |
| authorships[1].institutions[0].ror | https://ror.org/010ern194 |
| authorships[1].institutions[0].type | healthcare |
| authorships[1].institutions[0].lineage | https://openalex.org/I4210087417 |
| authorships[1].institutions[0].country_code | CN |
| authorships[1].institutions[0].display_name | Beijing Geriatric Hospital |
| authorships[1].institutions[1].id | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[1].institutions[1].ror | https://ror.org/013xs5b60 |
| authorships[1].institutions[1].type | education |
| authorships[1].institutions[1].lineage | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[1].institutions[1].country_code | CN |
| authorships[1].institutions[1].display_name | Capital Medical University |
| authorships[1].institutions[2].id | https://openalex.org/I4210115644 |
| authorships[1].institutions[2].ror | https://ror.org/029819q61 |
| authorships[1].institutions[2].type | government |
| authorships[1].institutions[2].lineage | https://openalex.org/I4210115644 |
| authorships[1].institutions[2].country_code | CN |
| authorships[1].institutions[2].display_name | Chinese Institute for Brain Research |
| authorships[1].author_position | middle |
| authorships[1].raw_author_name | Liyong Wu |
| authorships[1].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[1].raw_affiliation_strings | Beijing Key Laboratory of Geriatric Cognitive Disorders and Neurodegenerative, Beijing China, Beijing Key Laboratory of Geriatric Cognitive Disorders and Neurodegenerative, Beijing, China, Center of Alzheimer’s Disease, Beijing Institute for Brain Disorders, Beijing China, Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China |
| authorships[2].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5026787730 |
| authorships[2].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6221-1346 |
| authorships[2].author.display_name | Min Kyung Chu |
| authorships[2].countries | CN |
| authorships[2].affiliations[0].institution_ids | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[2].affiliations[0].raw_affiliation_string | Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China |
| authorships[2].institutions[0].id | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[2].institutions[0].ror | https://ror.org/013xs5b60 |
| authorships[2].institutions[0].type | education |
| authorships[2].institutions[0].lineage | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[2].institutions[0].country_code | CN |
| authorships[2].institutions[0].display_name | Capital Medical University |
| authorships[2].author_position | middle |
| authorships[2].raw_author_name | Min Chu |
| authorships[2].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[2].raw_affiliation_strings | Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China |
| authorships[3].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5037322205 |
| authorships[3].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3311-2901 |
| authorships[3].author.display_name | Yu Kong |
| authorships[3].countries | CN |
| authorships[3].affiliations[0].institution_ids | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[3].affiliations[0].raw_affiliation_string | department of neurology, XuanWu hospital, capital medical university, Beijing, China |
| authorships[3].institutions[0].id | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[3].institutions[0].ror | https://ror.org/013xs5b60 |
| authorships[3].institutions[0].type | education |
| authorships[3].institutions[0].lineage | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[3].institutions[0].country_code | CN |
| authorships[3].institutions[0].display_name | Capital Medical University |
| authorships[3].author_position | middle |
| authorships[3].raw_author_name | Yu Kong |
| authorships[3].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[3].raw_affiliation_strings | department of neurology, XuanWu hospital, capital medical university, Beijing, China |
| authorships[4].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5038487718 |
| authorships[4].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2172-7156 |
| authorships[4].author.display_name | Kexin Xie |
| authorships[4].countries | CN |
| authorships[4].affiliations[0].institution_ids | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[4].affiliations[0].raw_affiliation_string | Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China |
| authorships[4].institutions[0].id | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[4].institutions[0].ror | https://ror.org/013xs5b60 |
| authorships[4].institutions[0].type | education |
| authorships[4].institutions[0].lineage | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[4].institutions[0].country_code | CN |
| authorships[4].institutions[0].display_name | Capital Medical University |
| authorships[4].author_position | middle |
| authorships[4].raw_author_name | Kexin Xie |
| authorships[4].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[4].raw_affiliation_strings | Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China |
| authorships[5].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5061194998 |
| authorships[5].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4307-4133 |
| authorships[5].author.display_name | Yue Cui |
| authorships[5].countries | CN |
| authorships[5].affiliations[0].institution_ids | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[5].affiliations[0].raw_affiliation_string | Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China |
| authorships[5].institutions[0].id | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[5].institutions[0].ror | https://ror.org/013xs5b60 |
| authorships[5].institutions[0].type | education |
| authorships[5].institutions[0].lineage | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| authorships[5].institutions[0].country_code | CN |
| authorships[5].institutions[0].display_name | Capital Medical University |
| authorships[5].author_position | last |
| authorships[5].raw_author_name | Yue Cui |
| authorships[5].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[5].raw_affiliation_strings | Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China |
| has_content.pdf | True |
| has_content.grobid_xml | True |
| is_paratext | False |
| open_access.is_oa | True |
| open_access.oa_url | https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/alz.061751 |
| open_access.oa_status | bronze |
| open_access.any_repository_has_fulltext | False |
| created_date | 2025-10-10T00:00:00 |
| display_name | Genetic prion diseases presenting as frontotemporal lobar degeneration: clinical features and diagnostic challenge |
| has_fulltext | True |
| is_retracted | False |
| updated_date | 2025-11-06T03:46:38.306776 |
| primary_topic.id | https://openalex.org/T11335 |
| primary_topic.field.id | https://openalex.org/fields/13 |
| primary_topic.field.display_name | Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology |
| primary_topic.score | 0.9998000264167786 |
| primary_topic.domain.id | https://openalex.org/domains/1 |
| primary_topic.domain.display_name | Life Sciences |
| primary_topic.subfield.id | https://openalex.org/subfields/1312 |
| primary_topic.subfield.display_name | Molecular Biology |
| primary_topic.display_name | Prion Diseases and Protein Misfolding |
| related_works | https://openalex.org/W2139200429, https://openalex.org/W18892115, https://openalex.org/W2146281101, https://openalex.org/W4213299957, https://openalex.org/W2407057108, https://openalex.org/W2201605498, https://openalex.org/W4242333980, https://openalex.org/W2986249301, https://openalex.org/W1987626410, https://openalex.org/W1967187256 |
| cited_by_count | 0 |
| locations_count | 1 |
| best_oa_location.id | doi:10.1002/alz.061751 |
| best_oa_location.is_oa | True |
| best_oa_location.source.id | https://openalex.org/S108427512 |
| best_oa_location.source.issn | 1552-5260, 1552-5279 |
| best_oa_location.source.type | journal |
| best_oa_location.source.is_oa | False |
| best_oa_location.source.issn_l | 1552-5260 |
| best_oa_location.source.is_core | True |
| best_oa_location.source.is_in_doaj | False |
| best_oa_location.source.display_name | Alzheimer s & Dementia |
| best_oa_location.source.host_organization | https://openalex.org/P4310320595 |
| best_oa_location.source.host_organization_name | Wiley |
| best_oa_location.source.host_organization_lineage | https://openalex.org/P4310320595 |
| best_oa_location.source.host_organization_lineage_names | Wiley |
| best_oa_location.license | |
| best_oa_location.pdf_url | https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/alz.061751 |
| best_oa_location.version | publishedVersion |
| best_oa_location.raw_type | journal-article |
| best_oa_location.license_id | |
| best_oa_location.is_accepted | True |
| best_oa_location.is_published | True |
| best_oa_location.raw_source_name | Alzheimer's & Dementia |
| best_oa_location.landing_page_url | https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.061751 |
| primary_location.id | doi:10.1002/alz.061751 |
| primary_location.is_oa | True |
| primary_location.source.id | https://openalex.org/S108427512 |
| primary_location.source.issn | 1552-5260, 1552-5279 |
| primary_location.source.type | journal |
| primary_location.source.is_oa | False |
| primary_location.source.issn_l | 1552-5260 |
| primary_location.source.is_core | True |
| primary_location.source.is_in_doaj | False |
| primary_location.source.display_name | Alzheimer s & Dementia |
| primary_location.source.host_organization | https://openalex.org/P4310320595 |
| primary_location.source.host_organization_name | Wiley |
| primary_location.source.host_organization_lineage | https://openalex.org/P4310320595 |
| primary_location.source.host_organization_lineage_names | Wiley |
| primary_location.license | |
| primary_location.pdf_url | https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/alz.061751 |
| primary_location.version | publishedVersion |
| primary_location.raw_type | journal-article |
| primary_location.license_id | |
| primary_location.is_accepted | True |
| primary_location.is_published | True |
| primary_location.raw_source_name | Alzheimer's & Dementia |
| primary_location.landing_page_url | https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.061751 |
| publication_date | 2023-06-01 |
| publication_year | 2023 |
| referenced_works_count | 0 |
| abstract_inverted_index.4 | 119 |
| abstract_inverted_index.5 | 122, 162, 196 |
| abstract_inverted_index.8 | 164 |
| abstract_inverted_index.a | 167, 190 |
| abstract_inverted_index.23 | 92 |
| abstract_inverted_index.45 | 141 |
| abstract_inverted_index.In | 152 |
| abstract_inverted_index.as | 70 |
| abstract_inverted_index.be | 105, 307 |
| abstract_inverted_index.by | 40, 136, 260 |
| abstract_inverted_index.in | 19, 99, 118, 235, 246, 274 |
| abstract_inverted_index.is | 134, 258, 284 |
| abstract_inverted_index.of | 8, 34, 56, 61, 76, 85, 93, 170, 175, 193, 202, 210, 228, 267, 279, 286, 299 |
| abstract_inverted_index.on | 214, 221 |
| abstract_inverted_index.or | 127 |
| abstract_inverted_index.to | 21, 65, 104, 125, 179, 182, 297, 306 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(0% | 216 |
| abstract_inverted_index.1.1 | 198 |
| abstract_inverted_index.129 | 234, 273 |
| abstract_inverted_index.136 | 60 |
| abstract_inverted_index.EEG | 215 |
| abstract_inverted_index.MRI | 222 |
| abstract_inverted_index.The | 226, 276 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Val | 230, 269 |
| abstract_inverted_index.age | 139 |
| abstract_inverted_index.aid | 22 |
| abstract_inverted_index.and | 5, 26, 51, 59, 73, 145, 166, 172, 219 |
| abstract_inverted_index.for | 28, 232, 248, 271, 309 |
| abstract_inverted_index.had | 189 |
| abstract_inverted_index.our | 52, 66 |
| abstract_inverted_index.the | 3, 77, 108, 113, 229, 268, 287, 292 |
| abstract_inverted_index.two | 288 |
| abstract_inverted_index.vs. | 142, 150, 163, 197, 206, 217, 224, 251 |
| abstract_inverted_index.was | 240 |
| abstract_inverted_index.FTLD | 38, 58, 89, 126, 133, 157, 188, 239, 257, 283 |
| abstract_inverted_index.P39L | 111 |
| abstract_inverted_index.PRNP | 100, 236, 310 |
| abstract_inverted_index.been | 102 |
| abstract_inverted_index.data | 33, 75 |
| abstract_inverted_index.from | 48 |
| abstract_inverted_index.gene | 43 |
| abstract_inverted_index.have | 101 |
| abstract_inverted_index.high | 265 |
| abstract_inverted_index.most | 114 |
| abstract_inverted_index.need | 305 |
| abstract_inverted_index.rate | 169 |
| abstract_inverted_index.seen | 117 |
| abstract_inverted_index.than | 243 |
| abstract_inverted_index.that | 244, 298 |
| abstract_inverted_index.were | 46, 68, 80, 90, 95, 295 |
| abstract_inverted_index.with | 14, 37, 88, 107, 110, 121, 132, 156, 187, 238, 256, 282, 302 |
| abstract_inverted_index.61/60 | 143 |
| abstract_inverted_index.FTLD, | 109 |
| abstract_inverted_index.FTLD. | 180, 300 |
| abstract_inverted_index.GPrDs | 254, 280 |
| abstract_inverted_index.PRNP. | 275 |
| abstract_inverted_index.being | 112 |
| abstract_inverted_index.cases | 55, 84 |
| abstract_inverted_index.codon | 233, 272 |
| abstract_inverted_index.early | 23 |
| abstract_inverted_index.gPrDs | 35, 86, 130, 154, 185, 249 |
| abstract_inverted_index.lobar | 16 |
| abstract_inverted_index.lower | 208 |
| abstract_inverted_index.onset | 138 |
| abstract_inverted_index.order | 20 |
| abstract_inverted_index.prion | 10, 41, 62, 128, 176, 183 |
| abstract_inverted_index.rates | 201, 209 |
| abstract_inverted_index.these | 303 |
| abstract_inverted_index.which | 94 |
| abstract_inverted_index.while | 291 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(25.0% | 223 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(33.3% | 250 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(81.6% | 149 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(89.7% | 205 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(FTLD) | 18 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(PRNP) | 44 |
| abstract_inverted_index.3.3%), | 207 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Global | 32 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Method | 31 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Result | 82 |
| abstract_inverted_index.allele | 231, 270 |
| abstract_inverted_index.cases. | 123 |
| abstract_inverted_index.caused | 39 |
| abstract_inverted_index.closer | 296 |
| abstract_inverted_index.family | 147, 263 |
| abstract_inverted_index.groups | 79 |
| abstract_inverted_index.higher | 168, 200, 242 |
| abstract_inverted_index.longer | 191 |
| abstract_inverted_index.review | 50 |
| abstract_inverted_index.strong | 262 |
| abstract_inverted_index.years) | 144 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(gPrDs) | 12 |
| abstract_inverted_index.19.2%). | 252 |
| abstract_inverted_index.29.4%), | 218 |
| abstract_inverted_index.83.0%). | 225 |
| abstract_inverted_index.atrophy | 204 |
| abstract_inverted_index.earlier | 137 |
| abstract_inverted_index.feature | 7 |
| abstract_inverted_index.female. | 96 |
| abstract_inverted_index.genetic | 9 |
| abstract_inverted_index.history | 148 |
| abstract_inverted_index.protein | 42 |
| abstract_inverted_index.shorter | 159 |
| abstract_inverted_index.typical | 57 |
| abstract_inverted_index.years), | 165, 199 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(median: | 140, 161, 195 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Abstract | 0 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Clinical | 72 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Compared | 124, 181 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Patients | 301 |
| abstract_inverted_index.admitted | 64 |
| abstract_inverted_index.carriers | 237 |
| abstract_inverted_index.clinical | 4, 171, 277 |
| abstract_inverted_index.commonly | 115 |
| abstract_inverted_index.compared | 178 |
| abstract_inverted_index.diseases | 11, 63, 177 |
| abstract_inverted_index.distinct | 289 |
| abstract_inverted_index.duration | 160, 192 |
| abstract_inverted_index.families | 120 |
| abstract_inverted_index.features | 174, 278, 294 |
| abstract_inverted_index.genotype | 29, 311 |
| abstract_inverted_index.history, | 264 |
| abstract_inverted_index.included | 69 |
| abstract_inverted_index.periodic | 211 |
| abstract_inverted_index.records. | 53 |
| abstract_inverted_index.referral | 27 |
| abstract_inverted_index.reported | 103, 245 |
| abstract_inverted_index.stronger | 146 |
| abstract_inverted_index.symptoms | 194 |
| abstract_inverted_index.testing. | 30, 312 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Elucidate | 2 |
| abstract_inverted_index.addition, | 153 |
| abstract_inverted_index.ancillary | 6, 74, 173 |
| abstract_inverted_index.auxiliary | 293 |
| abstract_inverted_index.collected | 47 |
| abstract_inverted_index.compared. | 81 |
| abstract_inverted_index.complexes | 213 |
| abstract_inverted_index.controls. | 71 |
| abstract_inverted_index.different | 78 |
| abstract_inverted_index.diseases, | 129, 184 |
| abstract_inverted_index.exhibited | 158 |
| abstract_inverted_index.frequency | 227, 266 |
| abstract_inverted_index.mutations | 45, 98 |
| abstract_inverted_index.reported, | 116 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Background | 1 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Conclusion | 253 |
| abstract_inverted_index.associated | 106 |
| abstract_inverted_index.considered | 308 |
| abstract_inverted_index.diagnosis, | 25 |
| abstract_inverted_index.literature | 49, 247 |
| abstract_inverted_index.presenting | 13, 36, 87, 131, 155, 186, 255, 281 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Fifty‐one | 54 |
| abstract_inverted_index.conditions, | 290 |
| abstract_inverted_index.identified, | 91 |
| abstract_inverted_index.institution | 67 |
| abstract_inverted_index.27.5/13.2%). | 151 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Forty‐nine | 83 |
| abstract_inverted_index.degeneration | 17 |
| abstract_inverted_index.intermediate | 285 |
| abstract_inverted_index.short‐wave | 212 |
| abstract_inverted_index.characterized | 135, 259 |
| abstract_inverted_index.significantly | 241 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Twenty‐three | 97 |
| abstract_inverted_index.early‐onset, | 261 |
| abstract_inverted_index.frontotemporal | 15, 203 |
| abstract_inverted_index.hyperintensity | 220 |
| abstract_inverted_index.characteristics | 304 |
| abstract_inverted_index.identification, | 24 |
| cited_by_percentile_year | |
| corresponding_author_ids | https://openalex.org/A5056917368 |
| countries_distinct_count | 1 |
| institutions_distinct_count | 6 |
| corresponding_institution_ids | https://openalex.org/I183519381 |
| sustainable_development_goals[0].id | https://metadata.un.org/sdg/3 |
| sustainable_development_goals[0].score | 0.550000011920929 |
| sustainable_development_goals[0].display_name | Good health and well-being |
| citation_normalized_percentile.value | 0.2533393 |
| citation_normalized_percentile.is_in_top_1_percent | False |
| citation_normalized_percentile.is_in_top_10_percent | False |