Base-enhanced catalytic water oxidation by a carboxylate–bipyridine Ru(II) complex Article Swipe
Related Concepts
Catalysis
Carboxylate
Chemistry
Artificial photosynthesis
Redox
Water splitting
Catalytic oxidation
Phosphate buffered saline
Base (topology)
Ruthenium
Photochemistry
Inorganic chemistry
Stereochemistry
Organic chemistry
Photocatalysis
Mathematical analysis
Chromatography
Mathematics
Na Song
,
Javier J. Concepcion
,
Robert A. Binstead
,
Jennifer A. Rudd
,
Aaron K. Vannucci
,
Christopher J. Dares
,
Michael K. Coggins
,
Thomas J. Meyer
·
 YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1500245112
· OA: W2093879789
YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1500245112
· OA: W2093879789
 YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1500245112
· OA: W2093879789
YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1500245112
· OA: W2093879789
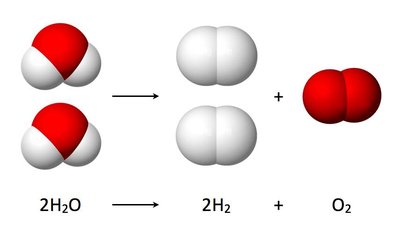
Significance Development of rapid, robust water oxidation catalysts remains an essential element in solar water splitting by artificial photosynthesis. We report here dramatic rate enhancements with added buffer bases for a robust Ru(II) polypyridyl catalyst with a calculated half-time for water oxidation of ∼7 μs in 1.0 M phosphate. The results of detailed kinetic studies provide insight into the water oxidation mechanism and an important role for added buffer bases in accelerating water oxidation by concerted atom–proton transfer.
Related Topics
Finding more related topics…