Basal autophagy maintains pancreatic acinar cell homeostasis and protein synthesis and prevents ER stress Article Swipe
Related Concepts
Laura Antonucci
,
Johan Bourghardt Fagman
,
Ju Youn Kim
,
Jelena Todoric
,
Ilya Gukovsky
,
Mason Mackey
,
Mark H. Ellisman
,
Michael Karin
·
 YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1519384112
· OA: W2249366289
YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1519384112
· OA: W2249366289
 YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1519384112
· OA: W2249366289
YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1519384112
· OA: W2249366289
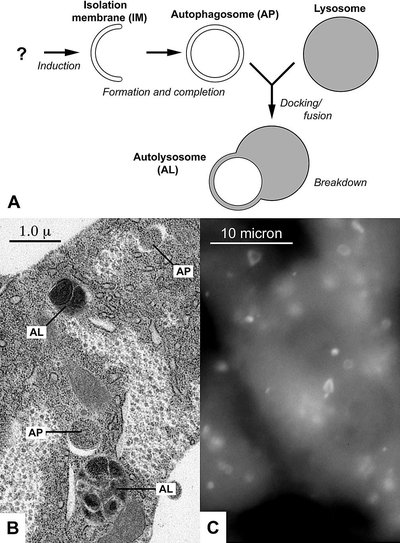
Significance This work identifies autophagy as an essential homeostatic process that maintains pancreatic acinar cell function. By preventing endoplasmic reticulum stress, reactive oxygen species accumulation, and DNA damage, basal autophagy preserves the high rates of protein synthesis that characterize the exocrine pancreas. Conversely, loss of autophagy can result in progressive loss of pancreatic function, which leads to development of pancreatitis as well as regenerative responses that may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer.
Related Topics
Finding more related topics…