Development of a symmetric echo planar imaging framework for clinical translation of rapid dynamic hyperpolarized 13C imaging Article Swipe
 YOU?
·
· 2016
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26123
· OA: W2285987116
YOU?
·
· 2016
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26123
· OA: W2285987116
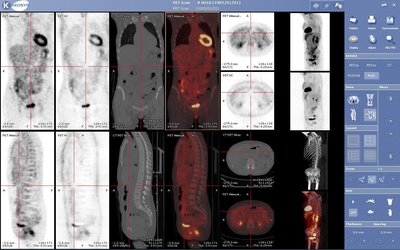
Purpose To develop symmetric echo planar imaging (EPI) and a reference scan framework for hyperpolarized 13 C metabolic imaging. Methods Symmetric, ramp‐sampled EPI with partial Fourier reconstruction was implemented on a 3T scanner. The framework for acquiring a reference scan on the 1 H channel and applied to 13 C data was described and validated in both phantoms and in vivo metabolism of [1‐ 13 C]pyruvate. Results Ramp‐sampled, symmetric EPI provided a substantial increase in the signal‐to‐noise ratio of the phantom experiments. The reference scan acquired on the 1 H channel yielded 13 C phantom images that varied in mean signal intensity <2%, compared with 13 C images reconstructed with a reference scan directly measured on the 13 C channel. The structural similarity index and dynamic time course from in vivo 13 C data further support the application of a 1 H reference scan to 13 C data to mitigate Nyquist ghost artifacts. Conclusion Ramp‐sampled, symmetric EPI with spectral‐spatial excitation of a single metabolite provides a fast, robust, and clinically efficacious approach to acquire hyperpolarized 13 C dynamic molecular imaging data. The gains of this efficient sampling, combined with partial Fourier methods, enables large matrix sizes required for human studies. Magn Reson Med 77:826–832, 2017. © 2016 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine