Fasciculoventricular accessory pathways following repair of ventricular septal defects Article Swipe
Related Concepts
Philip M. Chang
,
Akash Patel
,
Peter F. Aziz
,
Maully J. Shah
·
 YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrcr.2015.05.005
· OA: W2573259950
YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrcr.2015.05.005
· OA: W2573259950
 YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrcr.2015.05.005
· OA: W2573259950
YOU?
·
· 2015
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrcr.2015.05.005
· OA: W2573259950
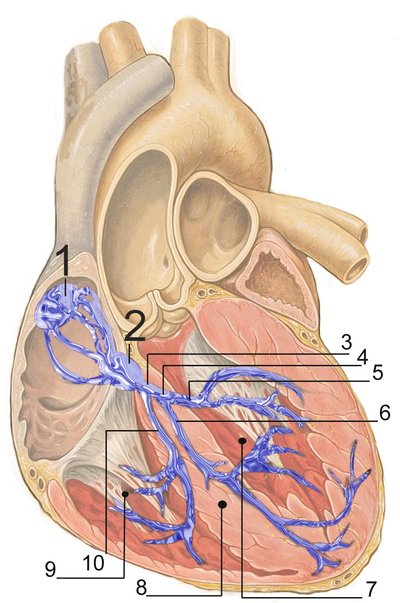
The most common form of preexcitation in the pediatric population is due to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) where atrioventricular (AV) conduction occurs partially or entirely through a congenital accessory AV bypass tract.1 Acquired WPW has been described when AV accessory pathways develop across suture lines after surgery for congenital heart disease (CHD).2–3 Fasciculoventricular (FV) pathways that manifest after CHD surgery have not been described previously. Although FV pathways do not participate in arrhythmias, their effects manifest as de novo preexcitation on surface electrocardiograms (ECGs).
Related Topics
Finding more related topics…