Diversity and Succession of Microbiota during Fermentation of the Traditional Indian Food Idli Article Swipe
Related Concepts
Fermentation
Biology
Leuconostoc
Food science
Leavening agent
Metagenomics
Weissella
Firmicutes
Population
Temperature gradient gel electrophoresis
Clostridium
Lactobacillus
Proteobacteria
Microbiology
Bacteria
Biochemistry
16S ribosomal RNA
Genetics
Demography
Gene
Sociology
Madhvi Mandhania
,
Dhiraj Paul
,
Mangesh Suryavanshi
,
Lokesh Sharma
,
Somak Chowdhury
,
Sonal S. Diwanay
,
Sham Diwanay
,
Yogesh S. Shouche
,
Milind S. Patole
·
 YOU?
·
· 2019
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00368-19
· OA: W2943084840
YOU?
·
· 2019
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00368-19
· OA: W2943084840
 YOU?
·
· 2019
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00368-19
· OA: W2943084840
YOU?
·
· 2019
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00368-19
· OA: W2943084840
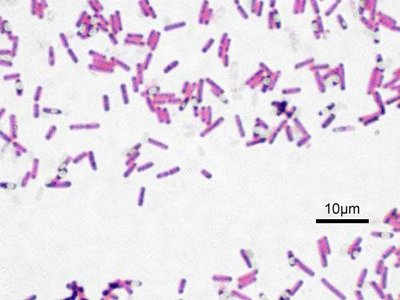
This is a comprehensive analysis of idli fermentation employing modern molecular tools which provided valuable information about the bacterial diversity enabling its fermentation. The study has demonstrated the relationship between the bacterial population and its functional role in the process. The nature of idli fermentation was found to be more complex than other food fermentations due to the succession of the bacterial population. Further studies using metatranscriptomics and metabolomics may enhance the understanding of this complex fermentation process. Moreover, the presence of microorganisms with beneficial properties plausibly makes idli a suitable functional food.
Related Topics
Finding more related topics…