Staphylococcus aureus Osteomyelitis: Bone, Bugs, and Surgery Article Swipe
Related Concepts
Osteomyelitis
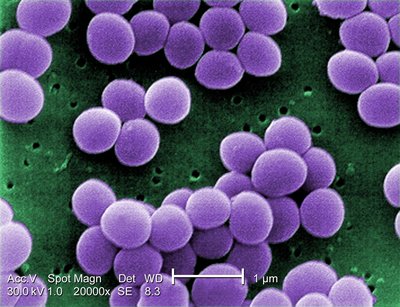
Staphylococcus aureus
Antimicrobial
Biology
Staphylococcal infections
Bone Infection
Innate immune system
Microbiology
Immune system
Immunology
Bacteria
Genetics
Kenneth L. Urish
,
James E. Cassat
·
 YOU?
·
· 2020
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.00932-19
· OA: W3008057925
YOU?
·
· 2020
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.00932-19
· OA: W3008057925
 YOU?
·
· 2020
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.00932-19
· OA: W3008057925
YOU?
·
· 2020
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.00932-19
· OA: W3008057925
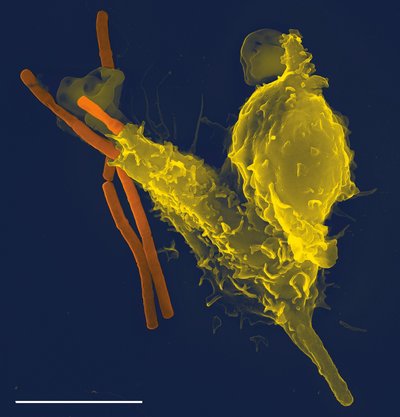
Osteomyelitis, or inflammation of bone, is most commonly caused by invasion of bacterial pathogens into the skeleton. Bacterial osteomyelitis is notoriously difficult to treat, in part because of the widespread antimicrobial resistance in the preeminent etiologic agent, the Gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus . Bacterial osteomyelitis triggers pathological bone remodeling, which in turn leads to sequestration of infectious foci from innate immune effectors and systemically delivered antimicrobials.
Related Topics
Finding more related topics…