Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Cucumis prophetarum Aqueous Leaf Extract and Their Antibacterial and Antiproliferative Activity Against Cancer Cell Lines Article Swipe
 YOU?
·
· 2020
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00155
· OA: W3009989320
YOU?
·
· 2020
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00155
· OA: W3009989320
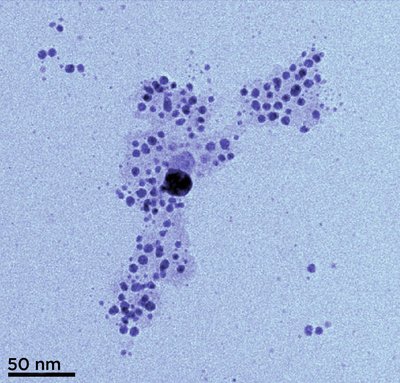
Biosynthesized nanoparticles are gaining attention because of biologically active plant secondary metabolites that help in green synthesis and also due to their unique biological applications. This study reports a facile, ecofriendly, reliable, and cost-effective synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the aqueous leaf extract of <i>Cucumis prophetarum</i> (<i>C. prophetarum</i>) and their antibacterial and antiproliferative activity. Silver nanoparticles were biosynthesized using the aqueous leaf extract of <i>C. prophetarum</i>, which acted as a reducing and capping agent. The biosynthesized <i>C. prophetarum</i> silver nanoparticles (Cp-AgNPs) were characterized using different techniques, such as UV-visible spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering (DLS), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX). Phytochemical analysis was performed to determine the phytochemicals responsible for the reduction and capping of the biosynthesized Cp-AgNPs. The antioxidant activity of the biosynthesized nanoparticles was determined using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) assays. Their antibacterial activity was checked against <i>Staphylococcus aureus</i> (Gram-positive) and <i>Salmonella typhi</i> (Gram-negative) bacteria. The biosynthesized nanoparticles showed dosage-dependent inhibition activity with a significant zone of inhibition and were more effective toward <i>S. typhi</i> as compared to <i>S. aureus</i>. Their antiproliferative activity was evaluated using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay on selected cancer cell lines. The IC<sub>50</sub> values of Cp-AgNPs on A549, MDA-MB-231, HepG2, and MCF-7 were found to be 105.8, 81.1, 94.2, and 65.6 μg/mL, respectively, and this showed that the Cp-AgNPs were more potent toward MCF-7 as compared to other cell lines used in this study. This work revealed that the biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using <i>C. prophetarum</i> leaf extract were associated with good antibacterial activity and antiproliferative potential against selected cancer cell lines. The biosynthesized <i>C. prophetarum</i> AgNPs can be further exploited as a potential candidate for antioxidant, antibacterial, and anticancer agents.