WOLFF-PARKINSON-WHITE SYNDROME Article Swipe
 YOU?
·
· 2020
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.46956/ijihd.vi.96
· OA: W3081703941
YOU?
·
· 2020
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.46956/ijihd.vi.96
· OA: W3081703941
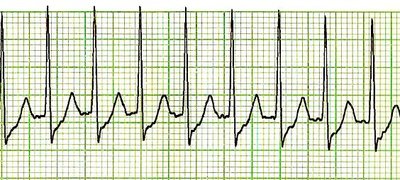
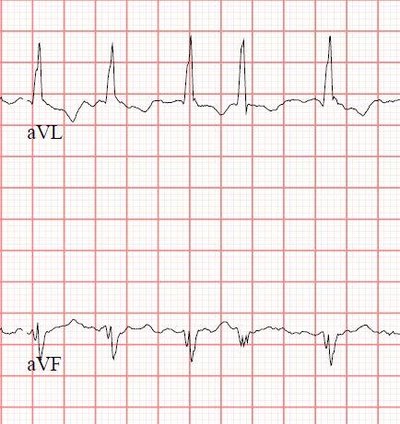
WPW syndrome is a congenital heart disease that is characterized by the presence of abnormal electrical connections between the atria and ventricles of the heart. In 1930, Louis Wolff, Sir John Parkinson, and Paul Dudley white published a seminal article describing the 11 young patients who suffered from attacks of tachycardia associated with an electrocardiographic pattern of ‘bundle branch block’ with a short PR interval. So from there onwards, it is called Wolff Parkinson white [WPW] syndrome. The normal conduction of the AV node occurs slowly than the accessory pathway conduction. Preexcitation is a process that the cardiac ventricles are activated earlier than the impulse of the AV node which leads to the shorter PR interval and formation of a delta wave. The supraventricular tachycardia associated with WPW syndrome is called AV reentrant or reciprocating tachycardia (AVRT).WPW syndrome is that there is an accessory pathway between the atrium and ventricles which cause rapid heartbeat or tachycardia.