Delta wave automatic mapping and catheter ablation without fluoroscopy in patients with overt accessory pathway: A new workflow Article Swipe
Related Concepts
Accessory pathway
Medicine
Cardiology
Internal medicine
Tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia
Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia
Ablation
Catheter ablation
Delta wave
WPW SYNDROME
Population
Electrocardiography
Non-rapid eye movement sleep
Environmental health
Ophthalmology
Eye movement
Saverio Iacopino
,
Jacopo Colella
,
Francesca Pesce
,
Paolo Artale
,
Gennaro Fabiano
,
Andrea Petretta
·
 YOU?
·
· 2021
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrcr.2021.06.015
· OA: W3178859331
YOU?
·
· 2021
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrcr.2021.06.015
· OA: W3178859331
 YOU?
·
· 2021
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrcr.2021.06.015
· OA: W3178859331
YOU?
·
· 2021
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrcr.2021.06.015
· OA: W3178859331
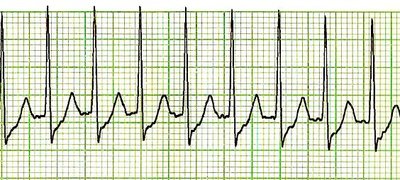
Accessory pathways (AP) are abnormal electrical connections between 2 parts of the heart, usually isolated one from the other. Atrioventricular AP may be responsible for atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), which accounts for about 30% of supraventricular tachycardias, being especially common in the pediatric population.1,2 When an AP is visible on a resting electrocardiogram (ECG) (ie, overt or manifest AP), it results in the so-called pre-excitation, which leads to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome when associated to tachyarrhythmias.
Related Topics
Finding more related topics…