Determination of Springs Constant by Hooke’s Law and Simple Harmonic Motion Experiment Article Swipe
 YOU?
·
· 2021
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2019/1/012053
· OA: W3210570174
YOU?
·
· 2021
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2019/1/012053
· OA: W3210570174
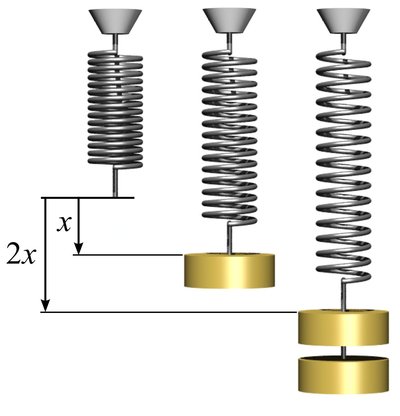
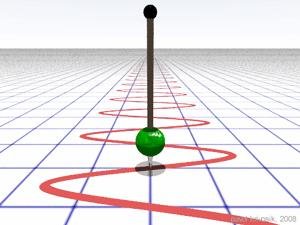
This study aims to calculate the spring constants of two types of stainless using Hooke’s Law principle and simple harmonic motion methods. Two types of springs (spring I and II) with different sizes in diameter have spring constant k values of 24 N/m and 5.4N/m, respectively. Based on the experiment and calculation, the spring constant of spring 1 calculated by Hooke’s Law and the simple harmonic motion experiment has an average value of 23.22 N/m with an error of 3.24% and 23.06 N/m with an error of 3.90%. On the other hand, the spring constant of spring 2 calculated by Hooke’s Law and the simple harmonic motion experiment has an average value of 5.47 N/m with an error of 1.44% and 5.32 N/m with an error of 1.48 %. Hence, we concluded that the determination of spring constant using Hooke’s Law has better accuracy.