Instance Reweighting Adversarial Training Based on Confused Label Article Swipe
 YOU?
·
· 2023
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241
YOU?
·
· 2023
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241
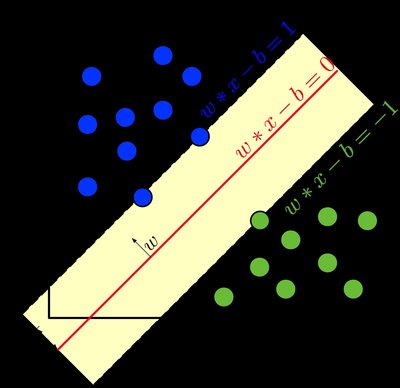
Reweighting adversarial examples during training plays an essential role in improving the robustness of neural networks, which lies in the fact that examples closer to the decision boundaries are much more vulnerable to being attacked and should be given larger weights. The probability margin (PM) method is a promising approach to continuously and path-independently measuring such closeness between the example and decision boundary. However, the performance of PM is limited due to the fact that PM fails to effectively distinguish the examples having only one misclassified category and the ones with multiple misclassified categories, where the latter is closer to multi-classification decision boundaries and is supported to be more critical in our observation. To tackle this problem, this paper proposed an improved PM criterion, called confused-label-based PM (CL-PM), to measure the closeness mentioned above and reweight adversarial examples during training. Specifically, a confused label (CL) is defined as the label whose prediction probability is greater than that of the ground truth label given a specific adversarial example. Instead of considering the discrepancy between the probability of the true label and the probability of the most misclassified label as the PM method does, we evaluate the closeness by accumulating the probability differences of all the CLs and ground truth label. CL-PM shares a negative correlation with data vulnerability: data with larger/smaller CL-PM is safer/riskier and should have a smaller/larger weight. Experiments demonstrated that CL-PM is more reliable in indicating the closeness regarding multiple misclassified categories, and reweighting adversarial training based on CL-PM outperformed state-of-the-art counterparts.
Related Topics
- Type
- article
- Language
- en
- Landing Page
- https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241
- OA Status
- hybrid
- Cited By
- 5
- References
- 17
- Related Works
- 10
- OpenAlex ID
- https://openalex.org/W4381956287
Raw OpenAlex JSON
- OpenAlex ID
-
https://openalex.org/W4381956287Canonical identifier for this work in OpenAlex
- DOI
-
https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241Digital Object Identifier
- Title
-
Instance Reweighting Adversarial Training Based on Confused LabelWork title
- Type
-
articleOpenAlex work type
- Language
-
enPrimary language
- Publication year
-
2023Year of publication
- Publication date
-
2023-01-01Full publication date if available
- Authors
-
Zhicong Qiu, Xianmin Wang, Huawei Ma, Songcao Hou, Jing Li, Zuoyong LiList of authors in order
- Landing page
-
https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241Publisher landing page
- Open access
-
YesWhether a free full text is available
- OA status
-
hybridOpen access status per OpenAlex
- OA URL
-
https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241Direct OA link when available
- Concepts
-
Closeness, Computer science, Adversarial system, Margin (machine learning), Decision boundary, Artificial intelligence, Robustness (evolution), Machine learning, Measure (data warehouse), Data mining, Mathematics, Support vector machine, Mathematical analysis, Chemistry, Gene, BiochemistryTop concepts (fields/topics) attached by OpenAlex
- Cited by
-
5Total citation count in OpenAlex
- Citations by year (recent)
-
2025: 2, 2024: 3Per-year citation counts (last 5 years)
- References (count)
-
17Number of works referenced by this work
- Related works (count)
-
10Other works algorithmically related by OpenAlex
Full payload
| id | https://openalex.org/W4381956287 |
|---|---|
| doi | https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241 |
| ids.doi | https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241 |
| ids.openalex | https://openalex.org/W4381956287 |
| fwci | 1.27721444 |
| type | article |
| title | Instance Reweighting Adversarial Training Based on Confused Label |
| biblio.issue | 2 |
| biblio.volume | 37 |
| biblio.last_page | 1256 |
| biblio.first_page | 1243 |
| topics[0].id | https://openalex.org/T11689 |
| topics[0].field.id | https://openalex.org/fields/17 |
| topics[0].field.display_name | Computer Science |
| topics[0].score | 0.9979000091552734 |
| topics[0].domain.id | https://openalex.org/domains/3 |
| topics[0].domain.display_name | Physical Sciences |
| topics[0].subfield.id | https://openalex.org/subfields/1702 |
| topics[0].subfield.display_name | Artificial Intelligence |
| topics[0].display_name | Adversarial Robustness in Machine Learning |
| topics[1].id | https://openalex.org/T12535 |
| topics[1].field.id | https://openalex.org/fields/17 |
| topics[1].field.display_name | Computer Science |
| topics[1].score | 0.9812999963760376 |
| topics[1].domain.id | https://openalex.org/domains/3 |
| topics[1].domain.display_name | Physical Sciences |
| topics[1].subfield.id | https://openalex.org/subfields/1702 |
| topics[1].subfield.display_name | Artificial Intelligence |
| topics[1].display_name | Machine Learning and Data Classification |
| topics[2].id | https://openalex.org/T11512 |
| topics[2].field.id | https://openalex.org/fields/17 |
| topics[2].field.display_name | Computer Science |
| topics[2].score | 0.9713000059127808 |
| topics[2].domain.id | https://openalex.org/domains/3 |
| topics[2].domain.display_name | Physical Sciences |
| topics[2].subfield.id | https://openalex.org/subfields/1702 |
| topics[2].subfield.display_name | Artificial Intelligence |
| topics[2].display_name | Anomaly Detection Techniques and Applications |
| is_xpac | False |
| apc_list | |
| apc_paid | |
| concepts[0].id | https://openalex.org/C2779545769 |
| concepts[0].level | 2 |
| concepts[0].score | 0.8717365264892578 |
| concepts[0].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q5135364 |
| concepts[0].display_name | Closeness |
| concepts[1].id | https://openalex.org/C41008148 |
| concepts[1].level | 0 |
| concepts[1].score | 0.7144616842269897 |
| concepts[1].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q21198 |
| concepts[1].display_name | Computer science |
| concepts[2].id | https://openalex.org/C37736160 |
| concepts[2].level | 2 |
| concepts[2].score | 0.6432616710662842 |
| concepts[2].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q1801315 |
| concepts[2].display_name | Adversarial system |
| concepts[3].id | https://openalex.org/C774472 |
| concepts[3].level | 2 |
| concepts[3].score | 0.49732688069343567 |
| concepts[3].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q6760393 |
| concepts[3].display_name | Margin (machine learning) |
| concepts[4].id | https://openalex.org/C42023084 |
| concepts[4].level | 3 |
| concepts[4].score | 0.4634217321872711 |
| concepts[4].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q5249231 |
| concepts[4].display_name | Decision boundary |
| concepts[5].id | https://openalex.org/C154945302 |
| concepts[5].level | 1 |
| concepts[5].score | 0.4615135192871094 |
| concepts[5].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q11660 |
| concepts[5].display_name | Artificial intelligence |
| concepts[6].id | https://openalex.org/C63479239 |
| concepts[6].level | 3 |
| concepts[6].score | 0.4405061602592468 |
| concepts[6].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q7353546 |
| concepts[6].display_name | Robustness (evolution) |
| concepts[7].id | https://openalex.org/C119857082 |
| concepts[7].level | 1 |
| concepts[7].score | 0.4342377781867981 |
| concepts[7].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q2539 |
| concepts[7].display_name | Machine learning |
| concepts[8].id | https://openalex.org/C2780009758 |
| concepts[8].level | 2 |
| concepts[8].score | 0.4332118630409241 |
| concepts[8].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q6804172 |
| concepts[8].display_name | Measure (data warehouse) |
| concepts[9].id | https://openalex.org/C124101348 |
| concepts[9].level | 1 |
| concepts[9].score | 0.2777533531188965 |
| concepts[9].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q172491 |
| concepts[9].display_name | Data mining |
| concepts[10].id | https://openalex.org/C33923547 |
| concepts[10].level | 0 |
| concepts[10].score | 0.22105777263641357 |
| concepts[10].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q395 |
| concepts[10].display_name | Mathematics |
| concepts[11].id | https://openalex.org/C12267149 |
| concepts[11].level | 2 |
| concepts[11].score | 0.16300243139266968 |
| concepts[11].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q282453 |
| concepts[11].display_name | Support vector machine |
| concepts[12].id | https://openalex.org/C134306372 |
| concepts[12].level | 1 |
| concepts[12].score | 0.0 |
| concepts[12].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q7754 |
| concepts[12].display_name | Mathematical analysis |
| concepts[13].id | https://openalex.org/C185592680 |
| concepts[13].level | 0 |
| concepts[13].score | 0.0 |
| concepts[13].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q2329 |
| concepts[13].display_name | Chemistry |
| concepts[14].id | https://openalex.org/C104317684 |
| concepts[14].level | 2 |
| concepts[14].score | 0.0 |
| concepts[14].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q7187 |
| concepts[14].display_name | Gene |
| concepts[15].id | https://openalex.org/C55493867 |
| concepts[15].level | 1 |
| concepts[15].score | 0.0 |
| concepts[15].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q7094 |
| concepts[15].display_name | Biochemistry |
| keywords[0].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/closeness |
| keywords[0].score | 0.8717365264892578 |
| keywords[0].display_name | Closeness |
| keywords[1].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/computer-science |
| keywords[1].score | 0.7144616842269897 |
| keywords[1].display_name | Computer science |
| keywords[2].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/adversarial-system |
| keywords[2].score | 0.6432616710662842 |
| keywords[2].display_name | Adversarial system |
| keywords[3].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/margin |
| keywords[3].score | 0.49732688069343567 |
| keywords[3].display_name | Margin (machine learning) |
| keywords[4].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/decision-boundary |
| keywords[4].score | 0.4634217321872711 |
| keywords[4].display_name | Decision boundary |
| keywords[5].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/artificial-intelligence |
| keywords[5].score | 0.4615135192871094 |
| keywords[5].display_name | Artificial intelligence |
| keywords[6].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/robustness |
| keywords[6].score | 0.4405061602592468 |
| keywords[6].display_name | Robustness (evolution) |
| keywords[7].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/machine-learning |
| keywords[7].score | 0.4342377781867981 |
| keywords[7].display_name | Machine learning |
| keywords[8].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/measure |
| keywords[8].score | 0.4332118630409241 |
| keywords[8].display_name | Measure (data warehouse) |
| keywords[9].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/data-mining |
| keywords[9].score | 0.2777533531188965 |
| keywords[9].display_name | Data mining |
| keywords[10].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/mathematics |
| keywords[10].score | 0.22105777263641357 |
| keywords[10].display_name | Mathematics |
| keywords[11].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/support-vector-machine |
| keywords[11].score | 0.16300243139266968 |
| keywords[11].display_name | Support vector machine |
| language | en |
| locations[0].id | doi:10.32604/iasc.2023.038241 |
| locations[0].is_oa | True |
| locations[0].source.id | https://openalex.org/S40639465 |
| locations[0].source.issn | 1079-8587, 2326-005X |
| locations[0].source.type | journal |
| locations[0].source.is_oa | False |
| locations[0].source.issn_l | 1079-8587 |
| locations[0].source.is_core | True |
| locations[0].source.is_in_doaj | False |
| locations[0].source.display_name | Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing |
| locations[0].source.host_organization | https://openalex.org/P4310320547 |
| locations[0].source.host_organization_name | Taylor & Francis |
| locations[0].source.host_organization_lineage | https://openalex.org/P4310320547 |
| locations[0].source.host_organization_lineage_names | Taylor & Francis |
| locations[0].license | cc-by |
| locations[0].pdf_url | |
| locations[0].version | publishedVersion |
| locations[0].raw_type | journal-article |
| locations[0].license_id | https://openalex.org/licenses/cc-by |
| locations[0].is_accepted | True |
| locations[0].is_published | True |
| locations[0].raw_source_name | Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing |
| locations[0].landing_page_url | https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241 |
| indexed_in | crossref |
| authorships[0].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5112457335 |
| authorships[0].author.orcid | |
| authorships[0].author.display_name | Zhicong Qiu |
| authorships[0].author_position | first |
| authorships[0].raw_author_name | Zhicong Qiu |
| authorships[0].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[1].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5020675795 |
| authorships[1].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3480-8780 |
| authorships[1].author.display_name | Xianmin Wang |
| authorships[1].author_position | middle |
| authorships[1].raw_author_name | Xianmin Wang |
| authorships[1].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[2].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5101790067 |
| authorships[2].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7432-5583 |
| authorships[2].author.display_name | Huawei Ma |
| authorships[2].author_position | middle |
| authorships[2].raw_author_name | Huawei Ma |
| authorships[2].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[3].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5101299897 |
| authorships[3].author.orcid | |
| authorships[3].author.display_name | Songcao Hou |
| authorships[3].author_position | middle |
| authorships[3].raw_author_name | Songcao Hou |
| authorships[3].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[4].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5107394996 |
| authorships[4].author.orcid | |
| authorships[4].author.display_name | Jing Li |
| authorships[4].author_position | middle |
| authorships[4].raw_author_name | Jing Li |
| authorships[4].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[5].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5091320821 |
| authorships[5].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0952-9915 |
| authorships[5].author.display_name | Zuoyong Li |
| authorships[5].author_position | last |
| authorships[5].raw_author_name | Zuoyong Li |
| authorships[5].is_corresponding | False |
| has_content.pdf | False |
| has_content.grobid_xml | False |
| is_paratext | False |
| open_access.is_oa | True |
| open_access.oa_url | https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241 |
| open_access.oa_status | hybrid |
| open_access.any_repository_has_fulltext | False |
| created_date | 2025-10-10T00:00:00 |
| display_name | Instance Reweighting Adversarial Training Based on Confused Label |
| has_fulltext | False |
| is_retracted | False |
| updated_date | 2025-11-06T03:46:38.306776 |
| primary_topic.id | https://openalex.org/T11689 |
| primary_topic.field.id | https://openalex.org/fields/17 |
| primary_topic.field.display_name | Computer Science |
| primary_topic.score | 0.9979000091552734 |
| primary_topic.domain.id | https://openalex.org/domains/3 |
| primary_topic.domain.display_name | Physical Sciences |
| primary_topic.subfield.id | https://openalex.org/subfields/1702 |
| primary_topic.subfield.display_name | Artificial Intelligence |
| primary_topic.display_name | Adversarial Robustness in Machine Learning |
| related_works | https://openalex.org/W4286235935, https://openalex.org/W1532734293, https://openalex.org/W4385154961, https://openalex.org/W4366257129, https://openalex.org/W1967777539, https://openalex.org/W3206792995, https://openalex.org/W1490526350, https://openalex.org/W4298643855, https://openalex.org/W3005055210, https://openalex.org/W3198488011 |
| cited_by_count | 5 |
| counts_by_year[0].year | 2025 |
| counts_by_year[0].cited_by_count | 2 |
| counts_by_year[1].year | 2024 |
| counts_by_year[1].cited_by_count | 3 |
| locations_count | 1 |
| best_oa_location.id | doi:10.32604/iasc.2023.038241 |
| best_oa_location.is_oa | True |
| best_oa_location.source.id | https://openalex.org/S40639465 |
| best_oa_location.source.issn | 1079-8587, 2326-005X |
| best_oa_location.source.type | journal |
| best_oa_location.source.is_oa | False |
| best_oa_location.source.issn_l | 1079-8587 |
| best_oa_location.source.is_core | True |
| best_oa_location.source.is_in_doaj | False |
| best_oa_location.source.display_name | Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing |
| best_oa_location.source.host_organization | https://openalex.org/P4310320547 |
| best_oa_location.source.host_organization_name | Taylor & Francis |
| best_oa_location.source.host_organization_lineage | https://openalex.org/P4310320547 |
| best_oa_location.source.host_organization_lineage_names | Taylor & Francis |
| best_oa_location.license | cc-by |
| best_oa_location.pdf_url | |
| best_oa_location.version | publishedVersion |
| best_oa_location.raw_type | journal-article |
| best_oa_location.license_id | https://openalex.org/licenses/cc-by |
| best_oa_location.is_accepted | True |
| best_oa_location.is_published | True |
| best_oa_location.raw_source_name | Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing |
| best_oa_location.landing_page_url | https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241 |
| primary_location.id | doi:10.32604/iasc.2023.038241 |
| primary_location.is_oa | True |
| primary_location.source.id | https://openalex.org/S40639465 |
| primary_location.source.issn | 1079-8587, 2326-005X |
| primary_location.source.type | journal |
| primary_location.source.is_oa | False |
| primary_location.source.issn_l | 1079-8587 |
| primary_location.source.is_core | True |
| primary_location.source.is_in_doaj | False |
| primary_location.source.display_name | Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing |
| primary_location.source.host_organization | https://openalex.org/P4310320547 |
| primary_location.source.host_organization_name | Taylor & Francis |
| primary_location.source.host_organization_lineage | https://openalex.org/P4310320547 |
| primary_location.source.host_organization_lineage_names | Taylor & Francis |
| primary_location.license | cc-by |
| primary_location.pdf_url | |
| primary_location.version | publishedVersion |
| primary_location.raw_type | journal-article |
| primary_location.license_id | https://openalex.org/licenses/cc-by |
| primary_location.is_accepted | True |
| primary_location.is_published | True |
| primary_location.raw_source_name | Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing |
| primary_location.landing_page_url | https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.038241 |
| publication_date | 2023-01-01 |
| publication_year | 2023 |
| referenced_works | https://openalex.org/W4379985863, https://openalex.org/W3133846602, https://openalex.org/W2804809630, https://openalex.org/W2564871102, https://openalex.org/W3120349939, https://openalex.org/W3119951344, https://openalex.org/W2930249865, https://openalex.org/W4210377582, https://openalex.org/W3047375952, https://openalex.org/W2981207549, https://openalex.org/W4226322346, https://openalex.org/W3006904074, https://openalex.org/W2883701651, https://openalex.org/W4312295151, https://openalex.org/W3023680410, https://openalex.org/W1608733719, https://openalex.org/W2964137095 |
| referenced_works_count | 17 |
| abstract_inverted_index.a | 47, 141, 163, 211, 226 |
| abstract_inverted_index.PM | 67, 75, 122, 126, 189 |
| abstract_inverted_index.To | 113 |
| abstract_inverted_index.an | 6, 120 |
| abstract_inverted_index.as | 147, 187 |
| abstract_inverted_index.be | 37, 107 |
| abstract_inverted_index.by | 196 |
| abstract_inverted_index.in | 9, 18, 110, 236 |
| abstract_inverted_index.is | 46, 68, 97, 104, 145, 153, 221, 233 |
| abstract_inverted_index.of | 13, 66, 157, 168, 175, 182, 201 |
| abstract_inverted_index.on | 249 |
| abstract_inverted_index.to | 24, 32, 50, 71, 77, 99, 106, 128 |
| abstract_inverted_index.we | 192 |
| abstract_inverted_index.CLs | 204 |
| abstract_inverted_index.The | 41 |
| abstract_inverted_index.all | 202 |
| abstract_inverted_index.and | 35, 52, 60, 87, 103, 134, 179, 205, 223, 244 |
| abstract_inverted_index.are | 28 |
| abstract_inverted_index.due | 70 |
| abstract_inverted_index.one | 84 |
| abstract_inverted_index.our | 111 |
| abstract_inverted_index.the | 11, 19, 25, 58, 64, 72, 80, 88, 95, 130, 148, 158, 170, 173, 176, 180, 183, 188, 194, 198, 203, 238 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(CL) | 144 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(PM) | 44 |
| abstract_inverted_index.data | 215, 217 |
| abstract_inverted_index.fact | 20, 73 |
| abstract_inverted_index.have | 225 |
| abstract_inverted_index.lies | 17 |
| abstract_inverted_index.more | 30, 108, 234 |
| abstract_inverted_index.most | 184 |
| abstract_inverted_index.much | 29 |
| abstract_inverted_index.ones | 89 |
| abstract_inverted_index.only | 83 |
| abstract_inverted_index.role | 8 |
| abstract_inverted_index.such | 55 |
| abstract_inverted_index.than | 155 |
| abstract_inverted_index.that | 21, 74, 156, 231 |
| abstract_inverted_index.this | 115, 117 |
| abstract_inverted_index.true | 177 |
| abstract_inverted_index.with | 90, 214, 218 |
| abstract_inverted_index.CL-PM | 209, 220, 232, 250 |
| abstract_inverted_index.above | 133 |
| abstract_inverted_index.based | 248 |
| abstract_inverted_index.being | 33 |
| abstract_inverted_index.does, | 191 |
| abstract_inverted_index.fails | 76 |
| abstract_inverted_index.given | 38, 162 |
| abstract_inverted_index.label | 143, 149, 161, 178, 186 |
| abstract_inverted_index.paper | 118 |
| abstract_inverted_index.plays | 5 |
| abstract_inverted_index.truth | 160, 207 |
| abstract_inverted_index.where | 94 |
| abstract_inverted_index.which | 16 |
| abstract_inverted_index.whose | 150 |
| abstract_inverted_index.called | 124 |
| abstract_inverted_index.closer | 23, 98 |
| abstract_inverted_index.during | 3, 138 |
| abstract_inverted_index.ground | 159, 206 |
| abstract_inverted_index.having | 82 |
| abstract_inverted_index.label. | 208 |
| abstract_inverted_index.larger | 39 |
| abstract_inverted_index.latter | 96 |
| abstract_inverted_index.margin | 43 |
| abstract_inverted_index.method | 45, 190 |
| abstract_inverted_index.neural | 14 |
| abstract_inverted_index.shares | 210 |
| abstract_inverted_index.should | 36, 224 |
| abstract_inverted_index.tackle | 114 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Instead | 167 |
| abstract_inverted_index.between | 57, 172 |
| abstract_inverted_index.defined | 146 |
| abstract_inverted_index.example | 59 |
| abstract_inverted_index.greater | 154 |
| abstract_inverted_index.limited | 69 |
| abstract_inverted_index.measure | 129 |
| abstract_inverted_index.weight. | 228 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(CL-PM), | 127 |
| abstract_inverted_index.However, | 63 |
| abstract_inverted_index.approach | 49 |
| abstract_inverted_index.attacked | 34 |
| abstract_inverted_index.category | 86 |
| abstract_inverted_index.confused | 142 |
| abstract_inverted_index.critical | 109 |
| abstract_inverted_index.decision | 26, 61, 101 |
| abstract_inverted_index.evaluate | 193 |
| abstract_inverted_index.example. | 166 |
| abstract_inverted_index.examples | 2, 22, 81, 137 |
| abstract_inverted_index.improved | 121 |
| abstract_inverted_index.multiple | 91, 241 |
| abstract_inverted_index.negative | 212 |
| abstract_inverted_index.problem, | 116 |
| abstract_inverted_index.proposed | 119 |
| abstract_inverted_index.reliable | 235 |
| abstract_inverted_index.reweight | 135 |
| abstract_inverted_index.specific | 164 |
| abstract_inverted_index.training | 4, 247 |
| abstract_inverted_index.weights. | 40 |
| abstract_inverted_index.boundary. | 62 |
| abstract_inverted_index.closeness | 56, 131, 195, 239 |
| abstract_inverted_index.essential | 7 |
| abstract_inverted_index.improving | 10 |
| abstract_inverted_index.measuring | 54 |
| abstract_inverted_index.mentioned | 132 |
| abstract_inverted_index.networks, | 15 |
| abstract_inverted_index.promising | 48 |
| abstract_inverted_index.regarding | 240 |
| abstract_inverted_index.supported | 105 |
| abstract_inverted_index.training. | 139 |
| abstract_inverted_index.boundaries | 27, 102 |
| abstract_inverted_index.criterion, | 123 |
| abstract_inverted_index.indicating | 237 |
| abstract_inverted_index.prediction | 151 |
| abstract_inverted_index.robustness | 12 |
| abstract_inverted_index.vulnerable | 31 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Experiments | 229 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Reweighting | 0 |
| abstract_inverted_index.adversarial | 1, 136, 165, 246 |
| abstract_inverted_index.categories, | 93, 243 |
| abstract_inverted_index.considering | 169 |
| abstract_inverted_index.correlation | 213 |
| abstract_inverted_index.differences | 200 |
| abstract_inverted_index.discrepancy | 171 |
| abstract_inverted_index.distinguish | 79 |
| abstract_inverted_index.effectively | 78 |
| abstract_inverted_index.performance | 65 |
| abstract_inverted_index.probability | 42, 152, 174, 181, 199 |
| abstract_inverted_index.reweighting | 245 |
| abstract_inverted_index.accumulating | 197 |
| abstract_inverted_index.continuously | 51 |
| abstract_inverted_index.demonstrated | 230 |
| abstract_inverted_index.observation. | 112 |
| abstract_inverted_index.outperformed | 251 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Specifically, | 140 |
| abstract_inverted_index.counterparts. | 253 |
| abstract_inverted_index.misclassified | 85, 92, 185, 242 |
| abstract_inverted_index.safer/riskier | 222 |
| abstract_inverted_index.larger/smaller | 219 |
| abstract_inverted_index.smaller/larger | 227 |
| abstract_inverted_index.vulnerability: | 216 |
| abstract_inverted_index.state-of-the-art | 252 |
| abstract_inverted_index.path-independently | 53 |
| abstract_inverted_index.confused-label-based | 125 |
| abstract_inverted_index.multi-classification | 100 |
| cited_by_percentile_year.max | 97 |
| cited_by_percentile_year.min | 95 |
| countries_distinct_count | 0 |
| institutions_distinct_count | 6 |
| sustainable_development_goals[0].id | https://metadata.un.org/sdg/16 |
| sustainable_development_goals[0].score | 0.7300000190734863 |
| sustainable_development_goals[0].display_name | Peace, Justice and strong institutions |
| citation_normalized_percentile.value | 0.80621105 |
| citation_normalized_percentile.is_in_top_1_percent | False |
| citation_normalized_percentile.is_in_top_10_percent | False |