Risk of Silico-Tuberculosis in Miners: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Article Swipe
 YOU?
·
· 2023
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/ijoem.ijoem_287_22
· OA: W4390471857
YOU?
·
· 2023
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/ijoem.ijoem_287_22
· OA: W4390471857
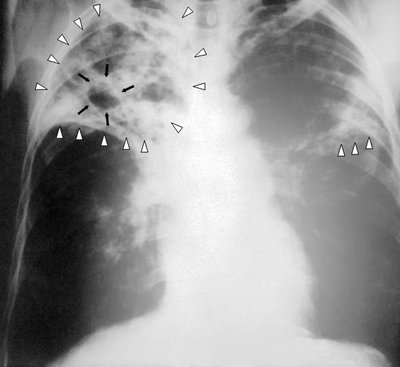
Context: Tuberculosis (TB) and Silicosis are public health problems with high morbidity and mortality. They also exist as comorbidities and are highly prevalent among mine workers. Aims: This study aims to estimate the risk of TB in miners with silicosis than in miners not having silicosis. Methods and Material: This systematic review was conducted by literature search using PubMed, and EMBASE for studies published from 1 st Jan 2017 till 20 th July 2022. From the data obtained using relevant keywords for the search, a total of 345 articles were selected for screening after applying our inclusion-exclusion criteria and removing duplicates. PRISMA guidelines were followed. items JBI critical appraisal checklist for cross-sectional studies was used for assessment of the risk of bias. The odds ratio was used to estimate the strength of the association. Results: After extensive screening, four studies have met our selection criteria. The meta-analysis of those studies revealed that the prevalence of TB in miners with silicosis is 27.11% while the prevalence of TB in miners with non-silicosis is 16.75%. The estimated pooled odds ratio (fixed effect model) is 1.34 (95% CI 1.01 – 1.76). Conclusions: The present study reveals that there is an increased risk of TB in miners with Silicosis. Newer initiatives must be taken to prevent TB in miners.