Shared genetic and environmental influences on altered functional connectivity and schizophrenia liability Article Swipe
 YOU?
·
· 2025
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1
YOU?
·
· 2025
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1
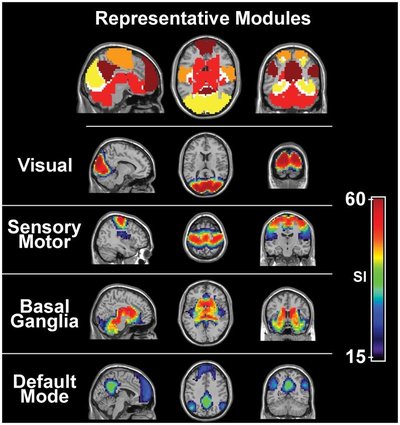
Schizophrenia is characterised by dysconnectivity of several resting-state functional brain networks, potentially reflecting reduced efficiency of brain communication. It remains unclear to what extent dysconnectivity is influenced by genetic or environmental liabilities to develop the disease. This study investigated whether such dysconnectivity indicates genetic liability or environmental risk of schizophrenia and its relation to cognitive functioning. Resting-state fMRI at 3T was measured in 71 individual twins discordant for schizophrenia and 154 individual matched healthy control twins. Functional connectivity was calculated within and between eight cortical networks and seven subcortical regions. Structural equation modelling assessed the heritability of connectivity, and its phenotypic, genetic, shared environmental and unique environmental associations with schizophrenia liability, as well as its relation to cognitive functioning. Phenotypic associations with increased schizophrenia liability were found in 12 connections (11%), with 8 showing hyperconnectivity and 4 hypo-connectivity. Two connections were partly explained by genetic overlap between disease liability and connectivity, i.e., hyperconnectivity of the sensorimotor-thalamic connection; hypoconnectivity of the sensorimotor-hippocampal connection. Five connections were partly explained by unique environmental overlap with schizophrenia liability, i.e., hyperconnectivity of the dorsal attention-thalamic, visual-thalamic and amygdala-accumbens connections; hypoconnectivity of the sensorimotor-hippocampal and default mode-salience connections. Increased hyperconnectivity was associated with lower cognitive functioning in this cohort enriched for schizophrenia. Dysconnectivity between functional brain networks is present with increased schizophrenia liability, with both hyper- and hypo-connectivity due to genetic and unique environmental influences. Hyperconnectivity between networks is related to lower cognitive functioning and may constitute a genetic or environmental marker for increased schizophrenia liability.
Related Topics
- Type
- article
- Language
- en
- Landing Page
- https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1
- OA Status
- gold
- Related Works
- 10
- OpenAlex ID
- https://openalex.org/W4413354225
Raw OpenAlex JSON
- OpenAlex ID
-
https://openalex.org/W4413354225Canonical identifier for this work in OpenAlex
- DOI
-
https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1Digital Object Identifier
- Title
-
Shared genetic and environmental influences on altered functional connectivity and schizophrenia liabilityWork title
- Type
-
articleOpenAlex work type
- Language
-
enPrimary language
- Publication year
-
2025Year of publication
- Publication date
-
2025-08-20Full publication date if available
- Authors
-
Karis Colyer‐Patel, Jalmar Teeuw, Rachel Brouwer, Marc M. Bohlken, Marc D. Binder, Wiepke Cahn, René S. Kahn, Hilleke E. Hulshoff PolList of authors in order
- Landing page
-
https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1Publisher landing page
- Open access
-
YesWhether a free full text is available
- OA status
-
goldOpen access status per OpenAlex
- OA URL
-
https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1Direct OA link when available
- Concepts
-
Schizophrenia (object-oriented programming), Liability, Functional connectivity, Neuroscience, Psychology, Business, Cognitive psychology, Psychiatry, FinanceTop concepts (fields/topics) attached by OpenAlex
- Cited by
-
0Total citation count in OpenAlex
- Related works (count)
-
10Other works algorithmically related by OpenAlex
Full payload
| id | https://openalex.org/W4413354225 |
|---|---|
| doi | https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1 |
| ids.doi | https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1 |
| ids.openalex | https://openalex.org/W4413354225 |
| fwci | 0.0 |
| type | article |
| title | Shared genetic and environmental influences on altered functional connectivity and schizophrenia liability |
| biblio.issue | |
| biblio.volume | |
| biblio.last_page | |
| biblio.first_page | |
| topics[0].id | https://openalex.org/T11577 |
| topics[0].field.id | https://openalex.org/fields/32 |
| topics[0].field.display_name | Psychology |
| topics[0].score | 0.8574000000953674 |
| topics[0].domain.id | https://openalex.org/domains/2 |
| topics[0].domain.display_name | Social Sciences |
| topics[0].subfield.id | https://openalex.org/subfields/3205 |
| topics[0].subfield.display_name | Experimental and Cognitive Psychology |
| topics[0].display_name | Cognitive Abilities and Testing |
| is_xpac | False |
| apc_list | |
| apc_paid | |
| concepts[0].id | https://openalex.org/C2776412080 |
| concepts[0].level | 2 |
| concepts[0].score | 0.7671606540679932 |
| concepts[0].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q7431605 |
| concepts[0].display_name | Schizophrenia (object-oriented programming) |
| concepts[1].id | https://openalex.org/C2777834853 |
| concepts[1].level | 2 |
| concepts[1].score | 0.6388865113258362 |
| concepts[1].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q96776939 |
| concepts[1].display_name | Liability |
| concepts[2].id | https://openalex.org/C3018011982 |
| concepts[2].level | 2 |
| concepts[2].score | 0.5696707367897034 |
| concepts[2].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q7316120 |
| concepts[2].display_name | Functional connectivity |
| concepts[3].id | https://openalex.org/C169760540 |
| concepts[3].level | 1 |
| concepts[3].score | 0.455011785030365 |
| concepts[3].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q207011 |
| concepts[3].display_name | Neuroscience |
| concepts[4].id | https://openalex.org/C15744967 |
| concepts[4].level | 0 |
| concepts[4].score | 0.3956562876701355 |
| concepts[4].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q9418 |
| concepts[4].display_name | Psychology |
| concepts[5].id | https://openalex.org/C144133560 |
| concepts[5].level | 0 |
| concepts[5].score | 0.3798736333847046 |
| concepts[5].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q4830453 |
| concepts[5].display_name | Business |
| concepts[6].id | https://openalex.org/C180747234 |
| concepts[6].level | 1 |
| concepts[6].score | 0.3284621238708496 |
| concepts[6].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q23373 |
| concepts[6].display_name | Cognitive psychology |
| concepts[7].id | https://openalex.org/C118552586 |
| concepts[7].level | 1 |
| concepts[7].score | 0.2311922013759613 |
| concepts[7].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q7867 |
| concepts[7].display_name | Psychiatry |
| concepts[8].id | https://openalex.org/C10138342 |
| concepts[8].level | 1 |
| concepts[8].score | 0.1317494809627533 |
| concepts[8].wikidata | https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q43015 |
| concepts[8].display_name | Finance |
| keywords[0].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/schizophrenia |
| keywords[0].score | 0.7671606540679932 |
| keywords[0].display_name | Schizophrenia (object-oriented programming) |
| keywords[1].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/liability |
| keywords[1].score | 0.6388865113258362 |
| keywords[1].display_name | Liability |
| keywords[2].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/functional-connectivity |
| keywords[2].score | 0.5696707367897034 |
| keywords[2].display_name | Functional connectivity |
| keywords[3].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/neuroscience |
| keywords[3].score | 0.455011785030365 |
| keywords[3].display_name | Neuroscience |
| keywords[4].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/psychology |
| keywords[4].score | 0.3956562876701355 |
| keywords[4].display_name | Psychology |
| keywords[5].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/business |
| keywords[5].score | 0.3798736333847046 |
| keywords[5].display_name | Business |
| keywords[6].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/cognitive-psychology |
| keywords[6].score | 0.3284621238708496 |
| keywords[6].display_name | Cognitive psychology |
| keywords[7].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/psychiatry |
| keywords[7].score | 0.2311922013759613 |
| keywords[7].display_name | Psychiatry |
| keywords[8].id | https://openalex.org/keywords/finance |
| keywords[8].score | 0.1317494809627533 |
| keywords[8].display_name | Finance |
| language | en |
| locations[0].id | doi:10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1 |
| locations[0].is_oa | True |
| locations[0].source | |
| locations[0].license | cc-by |
| locations[0].pdf_url | |
| locations[0].version | acceptedVersion |
| locations[0].raw_type | posted-content |
| locations[0].license_id | https://openalex.org/licenses/cc-by |
| locations[0].is_accepted | True |
| locations[0].is_published | False |
| locations[0].raw_source_name | |
| locations[0].landing_page_url | https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1 |
| indexed_in | crossref |
| authorships[0].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5005226164 |
| authorships[0].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6093-1507 |
| authorships[0].author.display_name | Karis Colyer‐Patel |
| authorships[0].author_position | first |
| authorships[0].raw_author_name | Karis Colyer-Patel |
| authorships[0].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[1].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5036898173 |
| authorships[1].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1637-888X |
| authorships[1].author.display_name | Jalmar Teeuw |
| authorships[1].author_position | middle |
| authorships[1].raw_author_name | Jalmar Teeuw |
| authorships[1].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[2].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5108625105 |
| authorships[2].author.orcid | |
| authorships[2].author.display_name | Rachel Brouwer |
| authorships[2].author_position | middle |
| authorships[2].raw_author_name | Rachel Brouwer |
| authorships[2].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[3].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5113829651 |
| authorships[3].author.orcid | |
| authorships[3].author.display_name | Marc M. Bohlken |
| authorships[3].author_position | middle |
| authorships[3].raw_author_name | Marc Bohlken |
| authorships[3].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[4].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5054306814 |
| authorships[4].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4255-5920 |
| authorships[4].author.display_name | Marc D. Binder |
| authorships[4].author_position | middle |
| authorships[4].raw_author_name | Marc De Hert |
| authorships[4].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[5].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5062319888 |
| authorships[5].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0482-8759 |
| authorships[5].author.display_name | Wiepke Cahn |
| authorships[5].author_position | middle |
| authorships[5].raw_author_name | Wiepke Cahn |
| authorships[5].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[6].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5031613969 |
| authorships[6].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5909-8004 |
| authorships[6].author.display_name | René S. Kahn |
| authorships[6].author_position | middle |
| authorships[6].raw_author_name | Rene Kahn |
| authorships[6].is_corresponding | False |
| authorships[7].author.id | https://openalex.org/A5001247088 |
| authorships[7].author.orcid | https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2038-5281 |
| authorships[7].author.display_name | Hilleke E. Hulshoff Pol |
| authorships[7].author_position | last |
| authorships[7].raw_author_name | Hilleke Hulshoff Pol |
| authorships[7].is_corresponding | False |
| has_content.pdf | False |
| has_content.grobid_xml | False |
| is_paratext | False |
| open_access.is_oa | True |
| open_access.oa_url | https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1 |
| open_access.oa_status | gold |
| open_access.any_repository_has_fulltext | False |
| created_date | 2025-10-10T00:00:00 |
| display_name | Shared genetic and environmental influences on altered functional connectivity and schizophrenia liability |
| has_fulltext | False |
| is_retracted | False |
| updated_date | 2025-11-06T03:46:38.306776 |
| primary_topic.id | https://openalex.org/T11577 |
| primary_topic.field.id | https://openalex.org/fields/32 |
| primary_topic.field.display_name | Psychology |
| primary_topic.score | 0.8574000000953674 |
| primary_topic.domain.id | https://openalex.org/domains/2 |
| primary_topic.domain.display_name | Social Sciences |
| primary_topic.subfield.id | https://openalex.org/subfields/3205 |
| primary_topic.subfield.display_name | Experimental and Cognitive Psychology |
| primary_topic.display_name | Cognitive Abilities and Testing |
| related_works | https://openalex.org/W2390354001, https://openalex.org/W2612097706, https://openalex.org/W2392804635, https://openalex.org/W1584150419, https://openalex.org/W4238444704, https://openalex.org/W1598740194, https://openalex.org/W47805238, https://openalex.org/W2765824783, https://openalex.org/W2388566552, https://openalex.org/W2798165684 |
| cited_by_count | 0 |
| locations_count | 1 |
| best_oa_location.id | doi:10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1 |
| best_oa_location.is_oa | True |
| best_oa_location.source | |
| best_oa_location.license | cc-by |
| best_oa_location.pdf_url | |
| best_oa_location.version | acceptedVersion |
| best_oa_location.raw_type | posted-content |
| best_oa_location.license_id | https://openalex.org/licenses/cc-by |
| best_oa_location.is_accepted | True |
| best_oa_location.is_published | False |
| best_oa_location.raw_source_name | |
| best_oa_location.landing_page_url | https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1 |
| primary_location.id | doi:10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1 |
| primary_location.is_oa | True |
| primary_location.source | |
| primary_location.license | cc-by |
| primary_location.pdf_url | |
| primary_location.version | acceptedVersion |
| primary_location.raw_type | posted-content |
| primary_location.license_id | https://openalex.org/licenses/cc-by |
| primary_location.is_accepted | True |
| primary_location.is_published | False |
| primary_location.raw_source_name | |
| primary_location.landing_page_url | https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/6s8wu_v1 |
| publication_date | 2025-08-20 |
| publication_year | 2025 |
| referenced_works_count | 0 |
| abstract_inverted_index.4 | 136 |
| abstract_inverted_index.8 | 132 |
| abstract_inverted_index.a | 241 |
| abstract_inverted_index.12 | 128 |
| abstract_inverted_index.3T | 59 |
| abstract_inverted_index.71 | 63 |
| abstract_inverted_index.It | 18 |
| abstract_inverted_index.as | 111, 113 |
| abstract_inverted_index.at | 58 |
| abstract_inverted_index.by | 3, 27, 143, 167 |
| abstract_inverted_index.in | 62, 127, 200 |
| abstract_inverted_index.is | 1, 25, 211, 232 |
| abstract_inverted_index.of | 5, 15, 48, 96, 153, 158, 176, 185 |
| abstract_inverted_index.or | 29, 45, 243 |
| abstract_inverted_index.to | 21, 32, 53, 116, 223, 234 |
| abstract_inverted_index.154 | 70 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Two | 138 |
| abstract_inverted_index.and | 50, 69, 81, 86, 98, 104, 135, 149, 181, 188, 220, 225, 238 |
| abstract_inverted_index.due | 222 |
| abstract_inverted_index.for | 67, 204, 246 |
| abstract_inverted_index.its | 51, 99, 114 |
| abstract_inverted_index.may | 239 |
| abstract_inverted_index.the | 34, 94, 154, 159, 177, 186 |
| abstract_inverted_index.was | 60, 78, 194 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Five | 162 |
| abstract_inverted_index.This | 36 |
| abstract_inverted_index.both | 218 |
| abstract_inverted_index.fMRI | 57 |
| abstract_inverted_index.risk | 47 |
| abstract_inverted_index.such | 40 |
| abstract_inverted_index.this | 201 |
| abstract_inverted_index.well | 112 |
| abstract_inverted_index.were | 125, 140, 164 |
| abstract_inverted_index.what | 22 |
| abstract_inverted_index.with | 108, 121, 131, 171, 196, 213, 217 |
| abstract_inverted_index.brain | 9, 16, 209 |
| abstract_inverted_index.eight | 83 |
| abstract_inverted_index.found | 126 |
| abstract_inverted_index.i.e., | 151, 174 |
| abstract_inverted_index.lower | 197, 235 |
| abstract_inverted_index.seven | 87 |
| abstract_inverted_index.study | 37 |
| abstract_inverted_index.twins | 65 |
| abstract_inverted_index.(11%), | 130 |
| abstract_inverted_index.cohort | 202 |
| abstract_inverted_index.dorsal | 178 |
| abstract_inverted_index.extent | 23 |
| abstract_inverted_index.hyper- | 219 |
| abstract_inverted_index.marker | 245 |
| abstract_inverted_index.partly | 141, 165 |
| abstract_inverted_index.shared | 102 |
| abstract_inverted_index.twins. | 75 |
| abstract_inverted_index.unique | 105, 168, 226 |
| abstract_inverted_index.within | 80 |
| abstract_inverted_index.between | 82, 146, 207, 230 |
| abstract_inverted_index.control | 74 |
| abstract_inverted_index.default | 189 |
| abstract_inverted_index.develop | 33 |
| abstract_inverted_index.disease | 147 |
| abstract_inverted_index.genetic | 28, 43, 144, 224, 242 |
| abstract_inverted_index.healthy | 73 |
| abstract_inverted_index.matched | 72 |
| abstract_inverted_index.overlap | 145, 170 |
| abstract_inverted_index.present | 212 |
| abstract_inverted_index.reduced | 13 |
| abstract_inverted_index.related | 233 |
| abstract_inverted_index.remains | 19 |
| abstract_inverted_index.several | 6 |
| abstract_inverted_index.showing | 133 |
| abstract_inverted_index.unclear | 20 |
| abstract_inverted_index.whether | 39 |
| abstract_inverted_index.assessed | 93 |
| abstract_inverted_index.cortical | 84 |
| abstract_inverted_index.disease. | 35 |
| abstract_inverted_index.enriched | 203 |
| abstract_inverted_index.equation | 91 |
| abstract_inverted_index.genetic, | 101 |
| abstract_inverted_index.measured | 61 |
| abstract_inverted_index.networks | 85, 210, 231 |
| abstract_inverted_index.regions. | 89 |
| abstract_inverted_index.relation | 52, 115 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Increased | 192 |
| abstract_inverted_index.cognitive | 54, 117, 198, 236 |
| abstract_inverted_index.explained | 142, 166 |
| abstract_inverted_index.increased | 122, 214, 247 |
| abstract_inverted_index.indicates | 42 |
| abstract_inverted_index.liability | 44, 124, 148 |
| abstract_inverted_index.modelling | 92 |
| abstract_inverted_index.networks, | 10 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Functional | 76 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Phenotypic | 119 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Structural | 90 |
| abstract_inverted_index.associated | 195 |
| abstract_inverted_index.calculated | 79 |
| abstract_inverted_index.constitute | 240 |
| abstract_inverted_index.discordant | 66 |
| abstract_inverted_index.efficiency | 14 |
| abstract_inverted_index.functional | 8, 208 |
| abstract_inverted_index.individual | 64, 71 |
| abstract_inverted_index.influenced | 26 |
| abstract_inverted_index.liability, | 110, 173, 216 |
| abstract_inverted_index.liability. | 249 |
| abstract_inverted_index.reflecting | 12 |
| abstract_inverted_index.connection. | 161 |
| abstract_inverted_index.connection; | 156 |
| abstract_inverted_index.connections | 129, 139, 163 |
| abstract_inverted_index.functioning | 199, 237 |
| abstract_inverted_index.influences. | 228 |
| abstract_inverted_index.liabilities | 31 |
| abstract_inverted_index.phenotypic, | 100 |
| abstract_inverted_index.potentially | 11 |
| abstract_inverted_index.subcortical | 88 |
| abstract_inverted_index.associations | 107, 120 |
| abstract_inverted_index.connections. | 191 |
| abstract_inverted_index.connections; | 183 |
| abstract_inverted_index.connectivity | 77 |
| abstract_inverted_index.functioning. | 55, 118 |
| abstract_inverted_index.heritability | 95 |
| abstract_inverted_index.investigated | 38 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Resting-state | 56 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Schizophrenia | 0 |
| abstract_inverted_index.characterised | 2 |
| abstract_inverted_index.connectivity, | 97, 150 |
| abstract_inverted_index.environmental | 30, 46, 103, 106, 169, 227, 244 |
| abstract_inverted_index.mode-salience | 190 |
| abstract_inverted_index.resting-state | 7 |
| abstract_inverted_index.schizophrenia | 49, 68, 109, 123, 172, 215, 248 |
| abstract_inverted_index.communication. | 17 |
| abstract_inverted_index.schizophrenia. | 205 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Dysconnectivity | 206 |
| abstract_inverted_index.dysconnectivity | 4, 24, 41 |
| abstract_inverted_index.visual-thalamic | 180 |
| abstract_inverted_index.hypoconnectivity | 157, 184 |
| abstract_inverted_index.Hyperconnectivity | 229 |
| abstract_inverted_index.hyperconnectivity | 134, 152, 175, 193 |
| abstract_inverted_index.hypo-connectivity | 221 |
| abstract_inverted_index.amygdala-accumbens | 182 |
| abstract_inverted_index.hypo-connectivity. | 137 |
| abstract_inverted_index.attention-thalamic, | 179 |
| abstract_inverted_index.sensorimotor-thalamic | 155 |
| abstract_inverted_index.sensorimotor-hippocampal | 160, 187 |
| cited_by_percentile_year | |
| countries_distinct_count | 0 |
| institutions_distinct_count | 8 |
| citation_normalized_percentile.value | 0.38935961 |
| citation_normalized_percentile.is_in_top_1_percent | False |
| citation_normalized_percentile.is_in_top_10_percent | True |