Spinal Anesthesia with Targeted Sedation based on Bispectral Index Values Compared with General Anesthesia with Masked Bispectral Index Values to Reduce Delirium: The SHARP Randomized Controlled Trial. Article Swipe
 YOU?
·
· 2021
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/aln.0000000000004015
YOU?
·
· 2021
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/aln.0000000000004015
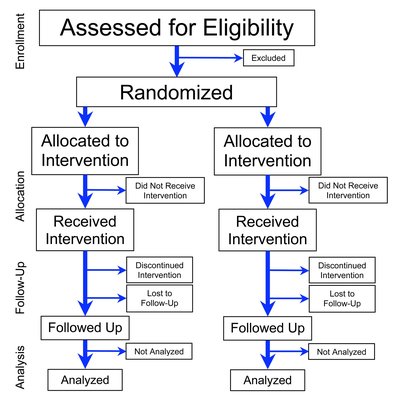
BACKGROUND: Reducing depth of anesthesia and anesthetic exposure may help prevent delirium, but trials have been conflicting. Most studies were conducted under general anesthesia or in cognitively-impaired patients. It is unclear whether reducing depth of anesthesia beyond levels consistent with general anesthesia reduces delirium in cognitively-intact patients. Our objective was to determine whether a bundled approach to reduce anesthetic agent exposure as determined by BIS values (spinal anesthesia with targeted sedation based on BIS values) compared with general anesthesia (masked BIS) reduces delirium. METHODS: Important eligibility criteria for this parallel-arm randomized trial were patients ≥65 years undergoing lumbar spine fusion. The intervention group received spinal anesthesia with targeted sedation to BIS>60–70. The control group received general anesthesia (masked BIS). The primary outcome was delirium using the Confusion Assessment Method daily through postoperative day 3, with blinded assessment. RESULTS: The median age of 217 patients in the analysis was 72 (interquartile range 69,77). Median BIS value in the spinal anesthesia with targeted sedation based on BIS values group was 62 (interquartile range 53,70) and in the general anesthesia with masked BIS values group was 45 (interquartile range 41,50, p<0.001). Incident delirium was not different in the spinal anesthesia with targeted sedation based on BIS values group (25.2%[28/111] vs. the general anesthesia with masked BIS values group (18.9%[20/106], p=0.259) (Relative Risk 1.22 [95%CI 0.85–1.76]). In pre-specified subgroup analyses, the effect of anesthetic strategy differed according to Mini-Mental State Examination, but not Charlson Comorbidity Index or age. Two strokes occurred among patients receiving spinal anesthesia and one death among patients receiving general anesthesia. CONCLUSIONS: Spinal anesthesia with targeted sedation based on BIS values compared with general anesthesia with masked BIS values did not reduce delirium after lumbar fusion.
Related Topics To Compare & Contrast
- Type
- article
- Language
- en
- Landing Page
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34666346
- OA Status
- green
- Cited By
- 27
- References
- 40
- Related Works
- 20
- OpenAlex ID
- https://openalex.org/W3207503229