A Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms for Intrusion\n Detection in Edge-Enabled IoT Networks Article Swipe
 YOU?
·
· 2021
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2111.01383
YOU?
·
· 2021
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2111.01383
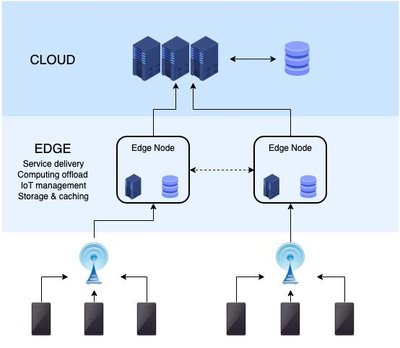
A significant increase in the number of interconnected devices and data\ncommunication through wireless networks has given rise to various threats,\nrisks and security concerns. Internet of Things (IoT) applications is deployed\nin almost every field of daily life, including sensitive environments. The edge\ncomputing paradigm has complemented IoT applications by moving the\ncomputational processing near the data sources. Among various security models,\nMachine Learning (ML) based intrusion detection is the most conceivable defense\nmechanism to combat the anomalous behavior in edge-enabled IoT networks. The ML\nalgorithms are used to classify the network traffic into normal and malicious\nattacks. Intrusion detection is one of the challenging issues in the area of\nnetwork security. The research community has proposed many intrusion detection\nsystems. However, the challenges involved in selecting suitable algorithm(s) to\nprovide security in edge-enabled IoT networks exist. In this paper, a\ncomparative analysis of conventional machine learning classification algorithms\nhas been performed to categorize the network traffic on NSL-KDD dataset using\nJupyter on Pycharm tool. It can be observed that Multi-Layer Perception (MLP)\nhas dependencies between input and output and relies more on network\nconfiguration for intrusion detection. Therefore, MLP can be more appropriate\nfor edge-based IoT networks with a better training time of 1.2 seconds and\ntesting accuracy of 79%.\n
Related Topics To Compare & Contrast


- Type
- preprint
- Landing Page
- http://arxiv.org/abs/2111.01383
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2111.01383
- OA Status
- green
- Cited By
- 3
- Related Works
- 10
- OpenAlex ID
- https://openalex.org/W4226105105