Using Statistical Properties and Random Forests, Classification Performance Model Evaluation for the Mental Arithmetic Task-Brain Computer Interface Article Swipe
 YOU?
·
· 2023
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.13052/rp-9788770040723.016
YOU?
·
· 2023
· Open Access
·
· DOI: https://doi.org/10.13052/rp-9788770040723.016
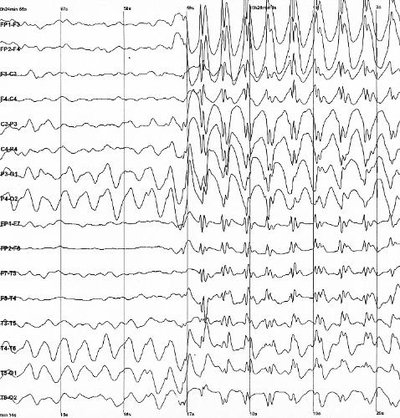
Ourobjective is to find an efficient method to classify the subject's mental cognitive workload as good or bad by obtaining features that can describe the continuous and underlying temporal dynamics of electroencephalography (EEG) data during the performance of mental tasks. To develop a BCI model that can forecast mental states like good and bad, we explore the ensemble learning technique using classifiers like the random forest classifier. From the alpha, beta, and gamma bands of EEG, the features like mean, root mean square, skewness, mode, data range, interquartile range (IQR), and three Hjorth parameters are extracted to differentiate a signal before-during mental arithmetic task. Our suggested model's analysis and results demonstrate that, when applying these techniques, accuracy is 96%. This model is further utilized for the application of automation in the Internet of Things (IoT).
Related Topics To Compare & Contrast
- Type
- article
- Language
- en
- Landing Page
- https://doi.org/10.13052/rp-9788770040723.016
- https://www.riverpublishers.com/pdf/ebook/chapter/RP_9788770040723C16.pdf
- OA Status
- gold
- References
- 14
- Related Works
- 10
- OpenAlex ID
- https://openalex.org/W4386704144