 The Expression Of The Emotions In Man And Animals
The Expression Of The Emotions In Man And Animals
Explore the cultural significance of The Expression Of The Emotions In Man And Animals through 12 virtual learning stations. Each station highlights a core theme and invites embodied understanding inside Second Life.
How-To (Simulacrics)
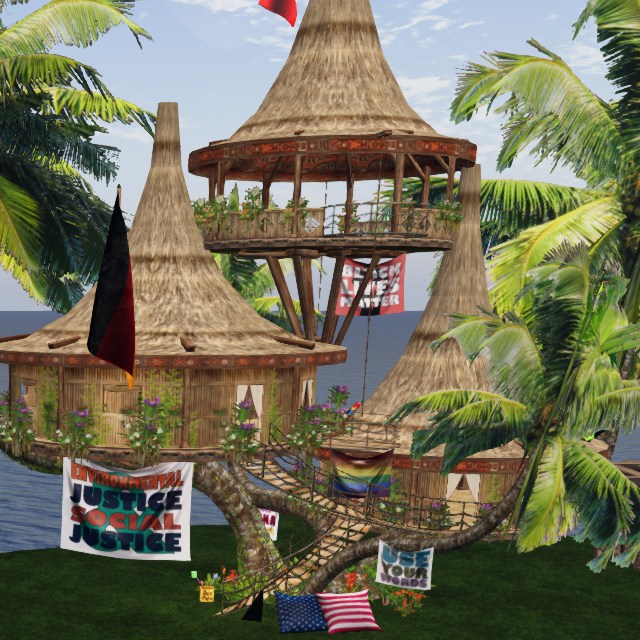




Nature & Cosmos
Ecology, systems, environment, awe
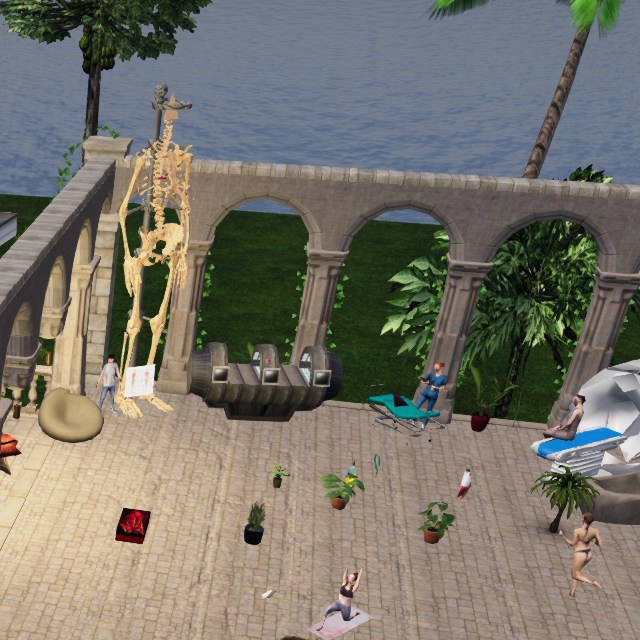

Body & Health
Biology, medicine, physicality, sex


Power & Control
Politics, governance, war, surveillance




Paradigms & Patterns
Models, systems, metaphors, meta-thinking
Epistemic Anchors for the Twelve Ontological Realms
Self & Identity
- Kant framed the self as a transcendental subject grounding consciousness and moral agency.
- Mead developed symbolic interactionism, showing how identity emerges through social interaction.
- Erikson mapped stages of identity development across the human lifespan.
Culture & Symbol
- Durkheim argued that collective representations form the basis of social cohesion.
- Geertz emphasized 'thick description' to interpret culture as webs of meaning.
- Barthes analyzed myths and semiotics to show how symbols construct ideology.
History & Memory
- Hegel saw history as a dialectical unfolding of Spirit through time.
- Halbwachs introduced the concept of collective memory shaped by social groups.
- Nora theorized lieux de mémoire as sites where memory crystallizes and endures.
Nature & Cosmos
- Spinoza conceived of nature as an immanent, self-sustaining whole.
- Von Humboldt unified scientific and aesthetic accounts of the cosmos.
- Lovelock proposed the Gaia hypothesis, viewing Earth as a self-regulating system.
Body & Health
- Descartes articulated the mind–body dualism that shaped modern medicine.
- Merleau-Ponty emphasized lived embodiment as central to perception.
- Foucault examined biopower and the medical gaze in shaping bodies and populations.
Economy & Work
- Marx theorized labor, capital, and exploitation as drivers of historical change.
- Weber analyzed rationalization and the Protestant ethic as forces in modern work.
- Polanyi argued that economies are embedded within social and cultural relations.
Power & Control
- Machiavelli explored power and statecraft as pragmatic strategies of control.
- Weber defined legitimate domination and authority types within political order.
- Foucault traced modern systems of discipline, surveillance, and biopolitics.
Learning & Knowing
- Plato grounded Western epistemology with his theory of forms and knowledge.
- Dewey advanced pragmatism, linking knowledge to experience and education.
- Freire promoted critical pedagogy as a practice of liberation through dialogue.
Technology & Tools
- Heidegger warned that technology enframes and reduces beings to resources.
- McLuhan argued that media shape perception, famously stating 'the medium is the message'.
- Haraway challenged boundaries between human, machine, and nature.
Imagination & Play
- Kant described the productive imagination as a bridge between sense and reason.
- Huizinga proposed play as a foundational element of culture in Homo Ludens.
- Vygotsky showed how play drives cognitive and social development in children.
Emotion & Expression
- Aristotle explained catharsis as the purgation of emotions through art and drama.
- Nietzsche contrasted Dionysian expression with Apollonian order in culture.
- Darwin studied how emotions are expressed biologically across humans and animals.
