Conjugate Transpose
Swipe Conjugate Transpose Vs...
Conjugate Transpose
Swipe Conjugate Transpose Vs...

Conjugate Transpose News
Description
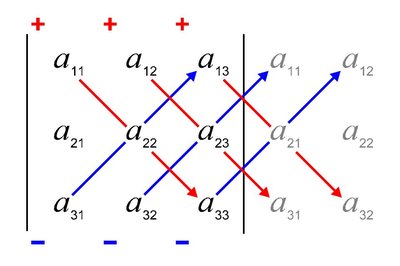
In mathematics, the conjugate transpose , also known as the Hermitian transpose , of an m × n {\displaystyle m\times n} complex matrix A {\displaystyle \mathbf {A} } is an n × m {\displaystyle n\times m} matrix obtained by transposing A {\displaystyle \mathbf {A} } and applying complex conjugate on each entry (the complex conjugate of a + i b {\displaystyle a+ib} being a − i b {\displaystyle a-ib} , for real numbers a {\displaystyle a} and b {\displaystyle b} ). It is often denoted as A H {\displaystyle \mathbf {A} ^{\mathrm {H} }} or A ∗ {\displaystyle \mathbf {A} ^{*}} or A ′ {\displaystyle \mathbf {A} '} or (often in physics) A † {\displaystyle \mathbf {A} ^{\dagger }} .
For real matrices, the conjugate transpose is just the transpose, A H = A T {\displaystyle \mathbf {A} ^{\mathrm {H} }=\mathbf {A} ^{\operatorname {T} }} .
Related
MoreTags
Collections
No collections available for this topic.
Details
- Slug: conjugate-transpose
- Total Views: 157
- Added: Jul 20, 2024