Description
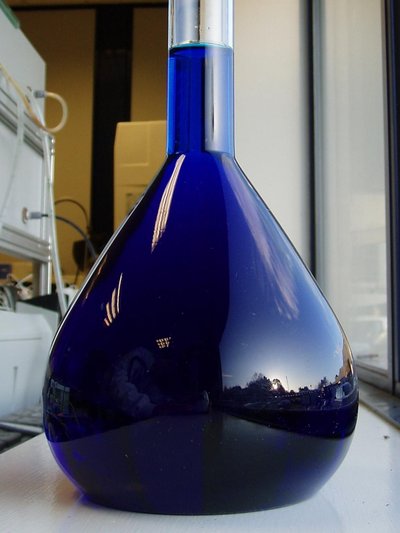
Copper(II) sulfate , also known as copper sulphate , is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuSO4. It forms hydrates CuSO4· n H2O, where n can range from 1 to 7. The pentahydrate ( n = 5), a bright blue crystal, is the most commonly encountered hydrate of copper(II) sulfate. Older names for the pentahydrate include blue vitriol , bluestone , vitriol of copper , and Roman vitriol. It exothermically dissolves in water to give the aquo complex [Cu(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry. The structure of the solid pentahydrate reveals a polymeric structure wherein copper is again octahedral but bound to four water ligands. The Cu(II)(H2O)4 centers are interconnected by sulfate anions to form chains. Anhydrous copper sulfate is a light grey powder.