Description
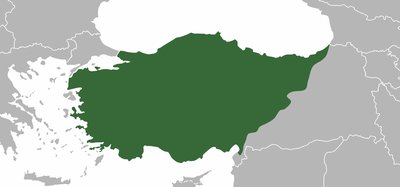
The Dying Gaul , also called The Dying Galatian (Italian: Galata Morente ) or The Dying Gladiator , is an ancient Roman marble semi- recumbent statue now in the Capitoline Museums in Rome. It is a copy of a now lost Greek sculpture from the Hellenistic period (323-31 BC) thought to have been made in bronze. The original may have been commissioned at some time between 230 and 220 BC by Attalus I of Pergamon to celebrate his victory over the Galatians, the Celtic or Gaulish people of parts of Anatolia. The original sculptor is believed to have been Epigonus, a court sculptor of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon.
Until the 20th century the marble statue was usually known as The Dying Gladiator , on the assumption that it depicted a wounded gladiator in a Roman amphitheatre. However, in the mid-19th century it was re-identified as a Gaul or Galatian and the present name "Dying Gaul" gradually achieved popular acceptance. The identification as a "barbarian" was evidenced for the figure's neck torc, thick hair and moustache, weapons and shield carved on the floor, and a type of Gallic carnyx between his legs.