Description
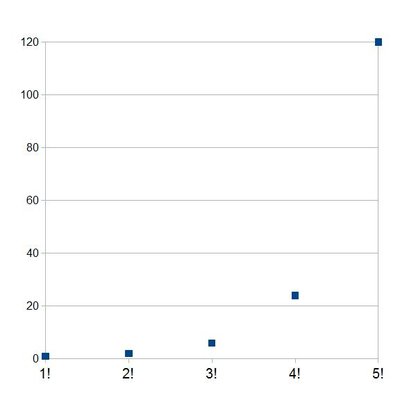
In mathematics, a geometric progression , also known as a geometric sequence , is a sequence of non-zero numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous one by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio. For example, the sequence 2, 6, 18, 54, ... is a geometric progression with common ratio 3. Similarly 10, 5, 2.5, 1.25, ... is a geometric sequence with common ratio 1/2.
Examples of a geometric sequence are powers r k of a fixed non-zero number r , such as 2 k and 3 k. The general form of a geometric sequence is
a , a r , a r 2 , a r 3 , a r 4 , … {\displaystyle a,\ ar,\ ar^{2},\ ar^{3},\ ar^{4},\ \ldots }
where r ≠ 0 is the common ratio and a ≠ 0 is a scale factor, equal to the sequence's start value. The sum of a geometric progression's terms is called a geometric series.
Geometric Progression News
Collections
No collections available for this topic.