Description
Ifá is a divination system and Yoruba religion that represents the teachings of the Orisha Ọrunmila. which makes use of an extensive corpus of texts and mathematical formulas, is practiced among Yoruba communities and African diaspora in South America and the Caribbean. The word Ifa refers to the mystical figure Ifa or Orunmila, regarded by the Yoruba as the deity of wisdom and intellectual development.
Its oracular literary body is made up of 256 volumes (signs) that are divided into two categories, the first called Ojú Odù or main Odù that consists of 16 chapters. The second category is composed of 240 chapters called Amúlù Odù (omoluos), these are composed through the combination of the main Odù.
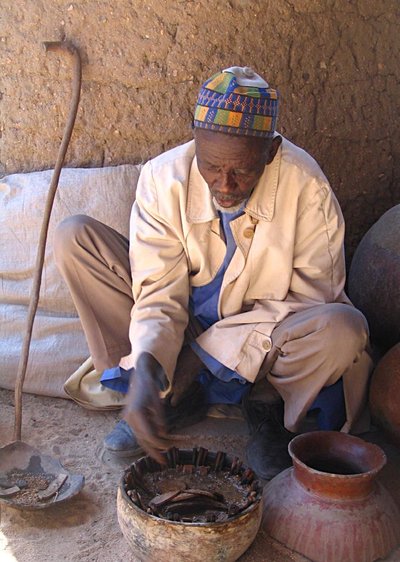
The system of divination used in Ifá is a code to access the scientific and metaphysical knowledge in the literary corpus, the Odu Ifá. Orunmila is identified as the Grand Priest, as he revealed (read; invented) the foundational divinity and prophecy (the first 16 Odu) to the world. Babalawos or Iyanifas are usually called Ifa priests, but really, they are scholars; the equivalent of professors in classical university systems. They use either the divining chain known as Opele , or the sacred palm ( Elaeis guineensis ) or kola nuts called Ikin , on the wooden divination tray called Opon Ifá to mathematically calculate which Odu to use for what problem.
Ifá is practiced throughout the Americas, West Africa, and the Canary Islands, in the form of a complex religious system, and plays a critical role in the traditions of Santería, Candomblé, Palo, Umbanda, Vodou, and other Afro- American faiths, as well as in some other traditional African religions.