Law Of Cosines
Swipe Law Of Cosines Vs...
Law Of Cosines
Swipe Law Of Cosines Vs...

Law Of Cosines News
Description
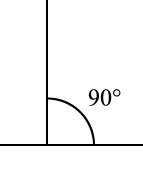
In trigonometry, the law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula or cosine rule ) relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. For a triangle with sides a , {\displaystyle a,} b , {\displaystyle b,} and c , {\displaystyle c,} opposite respective angles α , {\displaystyle \alpha ,} β , {\displaystyle \beta ,} and γ {\displaystyle \gamma } (see Fig. 1), the law of cosines states:
c 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2 a b cos γ , a 2 = b 2 + c 2 − 2 b c cos α , b 2 = a 2 + c 2 − 2 a c cos β . {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}c^{2}&=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab\cos \gamma ,\\\\[3mu]a^{2}&=b^{2}+c^{2}-2bc\cos \alpha ,\\\\[3mu]b^{2}&=a^{2}+c^{2}-2ac\cos \beta .\end{aligned}}}
The law of cosines generalizes the Pythagorean theorem, which holds only for right triangles: if γ {\displaystyle \gamma } is a right angle then cos γ = 0 , {\displaystyle \cos \gamma =0,} and the law of cosines reduces to c 2 = a 2 + b 2 . {\displaystyle c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}.}
The law of cosines is useful for solving a triangle when all three sides or two sides and their included angle are given.
Related
MoreTags
Collections
Details
- Slug: law-of-cosines
- Total Views: 416
- Added: Jul 20, 2024