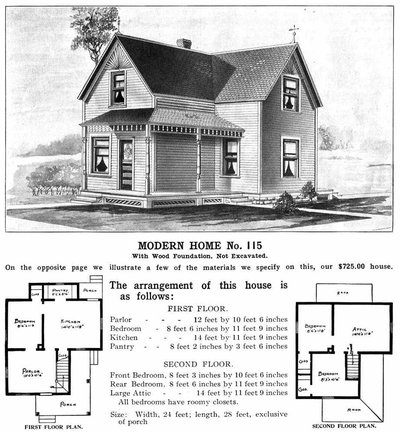
Description
In architecture, a loggia ( LOH -j(ee-)ə, usually UK: LOJ -(ee-)ə, Italian: [ˈlɔddʒa]) is a covered exterior gallery or corridor, usually on an upper level, but sometimes on the ground level of a building. The corridor is open to the elements because its outer wall is only partial, with the upper part usually supported by a series of columns or arches. An overhanging loggia may be supported by a baldresca.
From the early Middle Ages, nearly every Italian comune had an open arched loggia in its main square, which served as a "symbol of communal justice and government and as a stage for civic ceremony".
In Italian architecture, a loggia is also a small garden structure or house built on the roof of a residence, open on one or more sides, to enjoy cooling winds and the view. They were especially popular in the 17th century and are prominent in Rome and Bologna, Italy.
Loggia News
Tags
Collections
No collections available for this topic.