Description
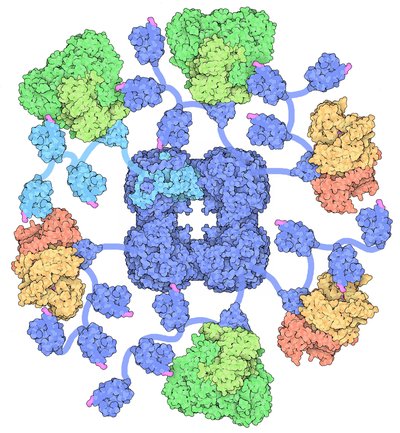
Photosystem II (or water-plastoquinone oxidoreductase ) is the first protein complex in the light-dependent reactions of oxygenic photosynthesis. It is located in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Within the photosystem, enzymes capture photons of light to energize electrons that are then transferred through a variety of coenzymes and cofactors to reduce plastoquinone to plastoquinol. The energized electrons are replaced by oxidizing water to form hydrogen ions and molecular oxygen.
By replenishing lost electrons with electrons from the splitting of water,
photosystem II provides the electrons for all of photosynthesis to occur. The
hydrogen ions (protons) generated by the oxidation of water help to create a
proton gradient that is used by ATP synthase to generate ATP. The energized
electrons transferred to plastoquinone are ultimately used to reduce NADP+
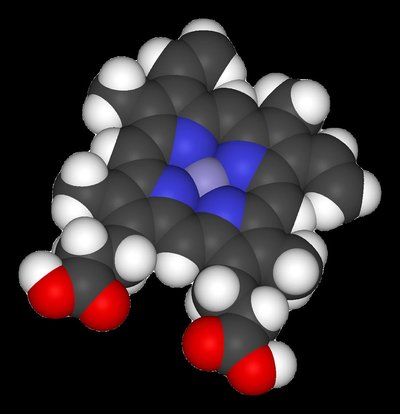
to NADPH or are used in non-cyclic electron flow. DCMU is a chemical often
used in laboratory settings to inhibit photosynthesis. When present, DCMU
inhibits electron flow from photosystem II to plastoquinone.
Photosystem Ii News
Tags
Collections
No collections available for this topic.