Description
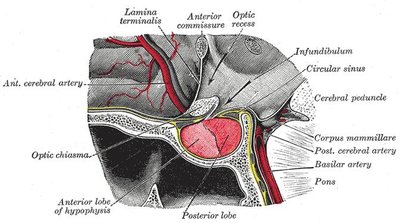
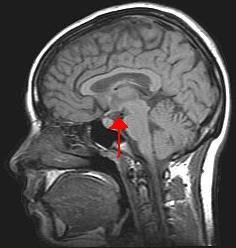
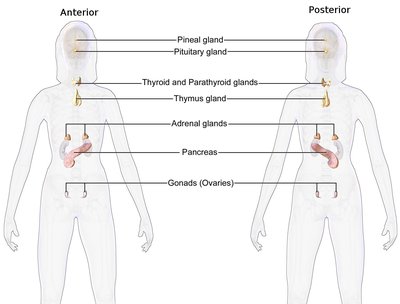
Sheehan's syndrome , also known as postpartum pituitary gland necrosis , occurs when the pituitary gland is damaged due to significant blood loss and hypovolemic shock (ischemic necrosis) usually during or after childbirth leading to decreased functioning of the pituitary gland (hypopituitarism). The pituitary gland is an endocrine organ, meaning it produces certain hormones and is involved in the regulation of various other hormones. This gland is located in the brain and sits in a pocket of the sphenoid bone known as the sella turcica. The pituitary gland works in conjunction with the hypothalamus, and other endocrine organs to modulate numerous bodily functions including growth, metabolism, menstruation, lactation, and even the "fight-or-flight" response. These endocrine organs release hormones in very specific pathways, known as hormonal axes. For example, the release of a hormone in the hypothalamus will target the pituitary to trigger the release of a subsequent hormone, and the pituitary's released hormone will target the next organ in the pathway. Hence, damage to the pituitary gland can have downstream effects on any of the aforementioned bodily functions.