Description
Tholins (after the Greek θολός ( _ _tholós__ ) "hazy" or "muddy"; from the
ancient Greek word meaning "sepia ink") are a wide variety of organic
compounds formed by solar ultraviolet or cosmic ray irradiation of simple
carbon-containing compounds such as carbon dioxide (CO
2), methane (CH
4) or ethane (C
2H
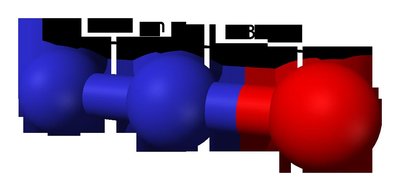
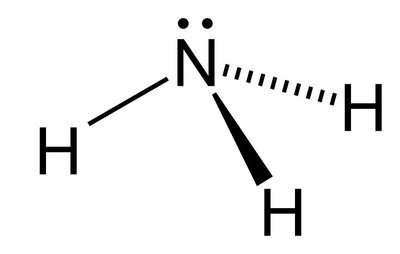
6), often in combination with nitrogen (N
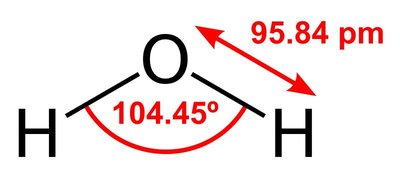
2) or water (H
2O). Tholins are disordered polymer-like materials made of repeating chains of
linked subunits and complex combinations of functional groups, typically
nitriles and hydrocarbons, and their degraded forms such as amines and
phenyls. Tholins do not form naturally on modern-day Earth, but they are found
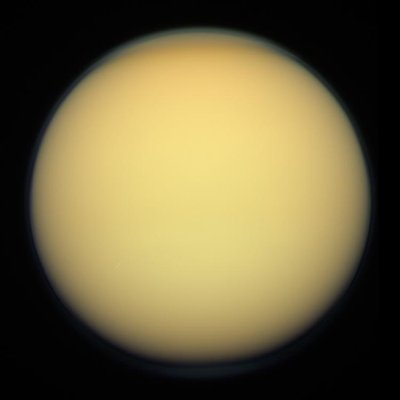
in great abundance on the surfaces of icy bodies in the outer Solar System,
and as reddish aerosols in the atmospheres of outer Solar System planets and
moons.
In the presence of water, tholins could be raw materials for prebiotic chemistry (i.e., the non-living chemistry that forms the basic chemicals of which life is made). Their existence has implications for the origins of life on Earth and possibly on other planets. As particles in an atmosphere, tholins scatter light, and can affect habitability.
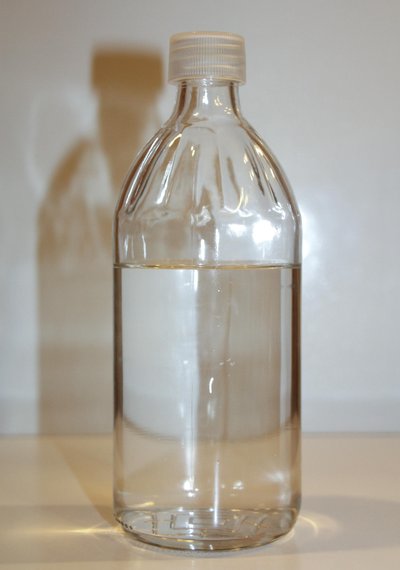
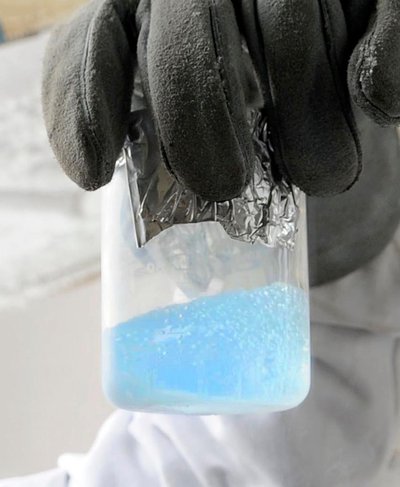
Tholins may be produced in a laboratory, and are usually studied as a heterogeneous mixture of many chemicals with many different structures and properties. Using techniques like thermogravimetric analysis, astrochemists analyze the composition of these tholin mixtures, and the exact character of the individual chemicals within them.